Designations on the map of minerals important in the study of geography. Always be in the mood Symbols of fossils on geographical maps
And with dots you can go to the symbols of various rocks and ways of their occurrence. It is known that there are sedimentary and igneous rocks. In this article we will study breed symbols these two types.
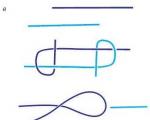
Sedimentary rocks usually occur in layers, while the latter usually occur in continuous masses. The most common sedimentary rocks: sands, sandstones, conglomerates, clays, shales, peat, coals, limestones, etc. The most common igneous: granites, diorites, diabases, basalts and lavas in general. Each of the rocks on the sections can be shown with symbols that to some extent resemble the rock depicted. For example, sands are always indicated by dots. It is more convenient to denote layered sands with dots, as indicated in Figure 1, I, and not layered sands, as in Figure 2, II. Methods of laying layers can be different: horizontal, inclined, etc. In accordance with this, strokes and dots are placed (Fig. 2, I and III). Sandstones are designated in much the same way as sands. Conglomerates consisting of rounded pebbles of various sizes are designated approximately as in Figure 3 A. Clays that do not have well-defined layering are designated by short horizontal strokes (Figure 3 B). Horizontal layers of layered clays - horizontal long strokes (Fig. 3 B). Figure 1 - Symbols of sands Figure 2 - Designation of different sands: I - layered clays,II- non-layered sands,III- cross-laminated clays
Clays with an admixture of sands- strokes and dots (Fig. 2 D). Clays with boulders- strokes and circles indicating boulders (Fig. 2 E).
Figure 2 - Designation of different sands: I - layered clays,II- non-layered sands,III- cross-laminated clays
Clays with an admixture of sands- strokes and dots (Fig. 2 D). Clays with boulders- strokes and circles indicating boulders (Fig. 2 E).  Figure 3 - Clay symbols Shales usually designated as layered clays, that is, by densely spaced long strokes drawn in the direction of the layers. Peat and coals usually depicted in solid black (Fig. 3 E). Limestone strata, which are almost always distinguished by the presence of a large number of vertical cracks, are depicted as bricks (Fig. 3 G).
Granites and other igneous rocks are most often indicated by rare crosses or corners (Fig. 4). Basalts, which quite often have a characteristic columnar structure, are depicted as dark vertical streaks, and sometimes simply as a dark mass, like other lavas.
Figure 3 - Clay symbols Shales usually designated as layered clays, that is, by densely spaced long strokes drawn in the direction of the layers. Peat and coals usually depicted in solid black (Fig. 3 E). Limestone strata, which are almost always distinguished by the presence of a large number of vertical cracks, are depicted as bricks (Fig. 3 G).
Granites and other igneous rocks are most often indicated by rare crosses or corners (Fig. 4). Basalts, which quite often have a characteristic columnar structure, are depicted as dark vertical streaks, and sometimes simply as a dark mass, like other lavas.  Figure 4 - Layered sedimentary rocks intruded by veins of igneous rocks Exercises using symbols of rocks are most conveniently carried out by constructing certain sections. They can be borrowed from any geology course.
Figure 4 - Layered sedimentary rocks intruded by veins of igneous rocks Exercises using symbols of rocks are most conveniently carried out by constructing certain sections. They can be borrowed from any geology course. Examples of breed symbols
After exercises with constructing diagrams and shading, we are able to build not only various kinds of profiles, but also sections. Let us give some of the most typical examples in order of increasing difficulty in drawing them (Fig. 5-9). Figure 5 - Monoclinal structure
Figure 5 - Monoclinal structure  Figure 6 - Remnant of the terrace (Katun River)
Figure 6 - Remnant of the terrace (Katun River)  Figure 7 - Cross section of the river terrace. Katun, (south of Michurinsk) Figure 8 - Cross section of moraines and intermoraine spaces
Figure 7 - Cross section of the river terrace. Katun, (south of Michurinsk) Figure 8 - Cross section of moraines and intermoraine spaces  Figure 9 - The northern slopes of the mountains are covered with forest, the southern ones are almost treeless (Altai)
Figure 9 - The northern slopes of the mountains are covered with forest, the southern ones are almost treeless (Altai) Our land is great and rich in various minerals!
In schools, from the very beginning of studying a subject such as geography, children are explained what wealth is extracted from the bowels of the earth. Children will learn in which part of the world certain natural resources can be found. A map with mineral symbols helps them with this.
The riches of our land
On a geographical map, topographers apply special symbols and signs indicating what exactly is located in a particular place. For example, forests are indicated as trees or in the form of a green rectangle, seas - in the form of a blue rectangle, sandy terrain - in yellow, and so on.
The earth is rich in such minerals as oil, gas, coal, peat, black ore, non-ferrous ore, lime, clay, sand, granite, precious stones (ruby, diamond, sapphire, emerald), fresh water, mineral water and so on. Thanks to topographers, people find out in which area gas or oil is produced, and much more.
According to the designations of mineral resources on the map of Russia, it is rich in oil and gas (Tyumen, Tomsk, Novosibirsk, Perm, Orenburg regions, the Republic of Tatarstan, Bashkortostan and so on), coal (Pechora, Kuznetsk, South Yakutsk basins), oil shale (St. -Petersburg deposit), peat (Northern Urals, Western Siberia), iron ores (Kursk), copper (Norilsk) and much more.
Students learn how minerals are mined, how they are cultivated, and how they need to be protected.
Symbols of mineral resources on the map
Each fossil has its own designation. Let's look at the most common ones:
- Coal is designated in the shape of a black square. Brown coal is a white square with diagonal black stripes. Oil shale is a black parallelogram. Oil is a black elongated trapezoid, similar to a triangle. Gas is the same symbol as oil, only white. Iron ore is a black triangle. Aluminum ores - a white circle inside a black square. Copper - black rectangle. Gold is a black and white circle, colored in half. Table salt - white cube.

Knowing what a particular symbol means, you can easily decipher any card.

Where and how it is mined: diamonds are mined from primary deposits (kimberlite and lamroite pipes) and secondary deposits - placers. There are about 35 diamond-mining countries in the world, the leading ones being Botswana, Russia, Canada, South Africa, Angola and Namibia. Deposits in Russia: Yakutia (80%), Arkhangelsk region (20%), Perm region.

Use in the economy: - in industry 80% (electrical, radio engineering, instrument making); -as detectors of nuclear radiation; -in medical meters; -in space research; -as a tool for cutting glass; - in jewelry. Distinctive features: -hardness; - compressive strength; - crack resistance; -resistance to aggressive environments; -has many shades. Useful properties: - under the influence of x-rays, ultraviolet and cathode rays, diamonds luminesce; - have a beneficial effect on the nervous system.


Where and how it is mined Peat is mined in an open way, because all peat deposits are located on the earth's surface. There are two main schemes for extracting peat: in relatively thin layers from the surface of the earth and in deep quarries to the entire depth of the peat layer. According to the first of these schemes, peat is extracted by cutting out the top layer, according to the second, using an excavator (or lump) method. Deposits in Russia: In Russia, the share of land occupied by peat bogs reaches 31.8% in the Tomsk region (Vasyugan swamps) and 12.5% in the Vologda region. There are also a large number of peat deposits in Central Russia (especially in the Ryazan, Moscow, and Vladimir regions).

Distinctive features Peat is crumbly and soft, like earth. Useful properties Improves soil structure and its water-air properties. Being the basis of the habitat of any plant and a moisture regulator, it provides optimal conditions for growth and development. Use on the farm Peat is used to fertilize the soil. In addition, peat is a high-energy household fuel (fireplace and grill fuel). In medicine, biochemistry, and industry, activated carbons are used as absorbents, filter elements, and gas absorbers of various kinds. Activated carbons are a product of deep processing of peat.


Where and how it is mined It is found in quartz veins. Widely distributed in metamorphic rocks: schists, gneisses, and marbles. Large deposits are formed as a result of pyrolysis of coal under the influence of traps on coal deposits. Deposits in Russia You can find graphite in Russia: Botogol deposit, Taiginskoe deposit, Kureyskoe deposit, Noginskoe deposit.

Distinctive features: graphite is soft, writes easily on paper, and has a more or less permanent, iron-black color. It can be confused with molybdenite. Unlike molybdenite, graphite can be ground into black dust with your fingers. Use in the household Graphite can be seen at home, pencils cannot write without it!


Deposits in Russia In Russia it is mined on the Kola Peninsula, in the Belgorod, Chelyabinsk, Kursk regions and in Karelia. It is mined mainly by open-pit mining. All necessary equipment is delivered to the deposit and a quarry is built. On average, the quarry is about 500 meters deep. Then they drill holes, put explosives in them and blow them up. Large excavators load the iron ore onto large machines and take it away for processing. Distribution of iron ore reserves by country: Ukraine - 18%, Russia -16%, China - 13%, Brazil - 13%, Australia - 11%, India - 4%, USA - 4%.



Where and how it is mined Yellow apatite is mined in Mexico and Canada; green - in India, Canada, Mozambique, Myanmar, Madagascar; purple - in Germany, Czech Republic; blue - in Myanmar, Brazil, Sri Lanka, Finland; blue-green - in Norway. In Russia, apatite is mined in the Baikal region and on the Kola Peninsula. They are mined in open pits and underground. For underground mining, horizontal mining adits are used. But in the Khibiny, miners working underground have to climb up rather than down to the adits. A large platform cage moves parallel to the mountainside, it brings miners to the desired level. Deposits in Russia The world's largest Khibinsky deposit on the Kola Peninsula, well-formed apatite crystals are mined in Transbaikalia from the Slyudyanka deposit.

Distinctive features The main diagnostic feature of apatite is the prismatic appearance of the crystals; It differs from similar beryl in less hardness. Useful properties Apatite is the main inorganic component of the bones and teeth of vertebrates and humans. Use on the farm Apatite is a raw material for the production of phosphate fertilizers, phosphorus and phosphoric acid; it is used in ferrous and non-ferrous metallurgy, in the production of ceramics and glass. Apatite is occasionally used by jewelers, but its widespread use in jewelry is impossible due to the low hardness of this stone and the fact that apatite is very fragile. Jewelry apatites are small in size - usually up to 5 carats, occasionally up to 20 carats, but they are of almost exclusively collector's interest. The largest gem-quality apatite crystal was found in Kenya and weighed 147 carats.


Where and how it is mined Methods of mining coal depend on the depth of its occurrence. 1) It is mined by open-pit mining in open-cast coal mines if the depth of the coal seam does not exceed 100 meters. 2) With the deepening of the coal mine, it is further profitable to develop the coal deposit using the underground method. Mines are used to extract coal from great depths. The deepest mines in the Russian Federation extract coal from a level of just over 1200 meters. Deposits in Russia: 1. Elginskoye field (Sakha). 2. Elegest deposit (Tuva). 3. Minusinsk coal basin (Republic of Khakassia). 4. Kuznetsk coal basin (Kuzbass).

Distinctive features The color is black, sometimes with steel-gray or dark gray. The luster is matte, silky, resinous to glassy and metallic. Dense, firmly connected. It is often fragile, easily splitting along numerous cracks into thick tiles or rectangular bars. Useful properties Contains volatile materials, ash and sulfur. Due to the high carbon content and relatively low humidity, the calorific value of coal reaches kcal/kg. The combustion temperature of coal is 470°C. Use on the farm Depending on its properties, coal is used as a household and energy fuel, as well as a raw material for the chemical and metallurgical industries. Rare trace elements are also extracted from it. Substances extracted from coal are used in the production of paints, plastics, medicines, etc. As a result of chemical processing of this mineral, more than 300 types of various industrial products are produced.


Where and how it is mined: in Germany, Canada, Norway, Greenland, USA, Great Britain, Italy, Tajikistan. The most abundant deposits of fluorite were discovered in Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan and Kazakhstan. open pit (quarry). Deposits in Russia The largest fluorite deposits are located in Transbaikalia: Abagaituy, Kalanguy (Chita region), deposits of Buryatia (Khuraiskoye, Ara-Tashirskoye and others). In addition to the Trans-Baikal group of deposits - Yaroslavl (Primorsky Territory), Amderma (Nenets Autonomous Okrug), etc.

Distinctive features: -transparent or translucent gemstone with a glassy sheen; -various colors: colorless, blue, pink, yellow, green, purple and almost black; -solid; -does not burn. Useful properties: -Fluorite is most often used as a remedy for headaches; -has a positive effect on the cardiovascular system and brain; - alleviates the condition of weather-dependent people; - normalizes sleep; -relieves the negative effects of stress; - affects the immune system. Use on the farm: 1. In metallurgy (making slag). 1. In the chemical industry (fluorine and artificial cryolite are produced for the production of aluminum). 3. In ceramic production - (for the production of enamels and glazes). 4. In medicine (in optics - for making lenses). 4. In jewelry production (for making jewelry).


Where and how it is mined: Gold is mined from the Urals to the Far East; even in the Moscow region there are several deposits with a small reserve of alluvial gold. Placer gold can be mined using the most primitive devices, from the well-known prospector's tray to a rattling pit made from an ordinary plastic barrel. Deposits in Russia: Aginskoye Amethyst Asachinskoye Baleyskoye Bamskoye Baranyevskoye Berezitovskoye Blagodatnoye Vasin Verninskoye Vorontsovskoye Gaiskoye Darasunskoye Zun-Kholbinskoye Itakinskoye Karalveemskoye Klyuchevskoye Kochkarskoye Dome Kuranakhskoye Kyuchusskoye Mayskoye Malomyrskoye Mnogovershinskoye Natalkinskoye Nezhdaninskoye Olimpiadinskoye Pioneer Pokrovskoye Rodnikovskoye Svetlinskoye Sukhoi Log Talaituyskoye Taseevskoye Khakanjinskoye Devil's Trough Eldorado

Distinctive features Small irregular grains, scales, plates, less often tree-like, thread-like formations, even more rarely distorted crystals of octahedral appearance. Beneficial properties Gold has a warming property, it is used for diseases of the nervous system, it improves cardiovascular activity, strengthens the heart muscle. This metal is useful to keep in the mouth to eliminate bad odor. This procedure protects the throat and nose from colds, helps with sore throat and other colds. Gold improves memory, intelligence and understanding, and gives energy to the heart. This noble metal is capable of disinfecting and killing microorganisms, so it is useful to wear gold jewelry during epidemics. Use in the household Gold is used to make dishes, jewelry, interior items, and is used in cosmetology, dentistry, electronics, and also in the chemical industry.


Where and how it is mined Nickel is common in nature, it is usually found in copper-nickel ores. The main deposits of nickel ores are located in Canada, Russia, Cuba, South Africa, New Caledonia and Ukraine. World onshore nickel reserves are estimated at 70 million tons. Nickel ores are mined mainly by quarrying (sometimes in mines), and then processed at metallurgical enterprises by smelting and beneficiation. Deposits in Russia: - Murmansk region - Norilsk region - Ural - Voronezh region In the Murmansk region there are two largest deposits of copper-nickel ores - Monchegorskoye and Pechengaskoye.

Distinctive features: ductile malleable metal of silver-white color. Beneficial properties Nickel is one of the microelements necessary for the normal development of living organisms. It is known that nickel takes part in enzymatic reactions in animals and plants. Pure nickel has very low thermal conductivity. Use on the farm: 1) nickel plating nickel plating is the creation of a nickel coating on the surface of another metal in order to protect it from corrosion; 2) production of batteries; production of iron-nickel, nickel-cadmium, nickel-zinc, nickel-hydrogen batteries; 3) medicine is used in the manufacture of braces and prosthetics; 5) coinage Nickel is widely used in the production of coins in many countries; 6) heat insulators are used for the manufacture of various types of holders of heated objects; 7) The music industry is used to produce winding strings for musical instruments.


Where and how it is mined Native platinum is mined at mines (see the article Noble Metals for more details); placer deposits of platinum are less rich, which are explored mainly by the method of spot sampling. Deposits in Russia In Russia, platinum was first discovered in the Urals, in the Verkh-Isetsky district, in 1819. When washing gold-bearing rocks, white shiny grains were noticed in the gold, which did not dissolve even in the strongest acids. Subsequently, new finds appeared, for example, in 1822 in alluvial gold from the Nevyansk and Bilimbaevsky mines.

Distinctive features Heavy, soft silvery-white metal. Beneficial properties Anti-inflammatory, preventing the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria and their attack on healthy organs; transport, as a result of which useful elements are distributed throughout the body to where it is especially needed; regenerating, thanks to which the healing of damage to the epidermis occurs faster, and the skin of a mature person is successfully freed from the accumulation of harmful toxins. Household use Platinum compounds (mainly aminoplatinates) are used as cytostatics in the treatment of various forms of cancer. Cisplatin (cis-dichlorodiammineplatinum(II)) was the first to be introduced into clinical practice; however, more effective carboxylate complexes of diammineplatinum, carboplatin and oxaliplatin, are currently used.


Where and how it is mined The largest producers of bauxite are Australia, Guinea, Jamaica and Brazil. The main aluminum ore, bauxite, is mined mainly in quarries. Typically, a layer of ore is blasted to form a working platform at a depth of up to 20 m, and then removed. The ore pieces are crushed and sorted using screens and classifiers. The crushed ore is further beneficiated and the waste rock (tailings) is discarded. Bayer process. The process of producing pure alumina involves heating bauxite with caustic soda, filtering, precipitating the aluminum hydroxide and calcining it to release pure alumina. Hall-Heroux electrolysis. The final stage of aluminum production involves its electrolytic reduction from pure alumina obtained in the Bayer process. This method of extracting aluminum is based on the fact (discovered by Hall and Heroux) that when alumina is dissolved in molten cryolite, aluminum is released during electrolysis of the solution. Deposits in Russia: OJSC Sevuralboxitruda Kalinskoye (Sverdlovsk region) Krasnaya Shapochka (Sverdlovsk region) Novokalinskoye (Sverdlovsk region) Cheremukhovskoye (Sverdlovsk region) OJSC Bauxite Timan Vezhayu-Vorykvinskoye (Komi Republic) OJSC Severo-Onezhsky bauxite mine Iksinskoye (Arkhangelsk region) Unallocated fund Vislovskoye (Belgorod region)

Distinctive features: lightweight, paramagnetic metal of silver-white color, easy to form, cast, and machine. Aluminum has high thermal and electrical conductivity and resistance to corrosion due to the rapid formation of strong oxide films that protect the surface from further interaction. Useful properties Malleable and plastic, aluminum easily takes any shape. The oxide film makes it resistant to corrosion, which means the service life of aluminum products can be very long. In addition, high electrical conductivity, non-toxicity and ease of processing must be added to the list of advantages. Household use About 28% of aluminum produced is used to make beverage cans, food containers and all kinds of packaging. Another 17% is used in vehicles, including aircraft, military equipment, railroad cars and automobiles. About 16% is used in building structures. About 8% is used in high-voltage power lines and other electrical devices, and 7% in consumer products such as refrigerators, air conditioners, washing machines and furniture. 6% is spent on the needs of mechanical engineering and industrial equipment. The remainder of the aluminum consumed is used in the production of television antennas, pigments and paints, spacecraft and ships.



Distinctive features: the plasticity of clay dough, i.e. the ability to take and maintain any shape in its raw form, the ability to retain this shape after “drying” with a decrease in volume, stickiness. Beneficial properties In folk medicine, many different diseases have been treated with clay at all times. They made lotions, compresses, and powders from it. They took it internally to cleanse their body of poisons and harmful substances. Clay was used to relieve headaches, depression, and allergies. Use on the farm Clay is used as a building material, used in the form of baked bricks. Various products are made from clay dough: jugs, krinks, pots, bowls, etc., which after firing become completely hard and do not allow water to pass through.


Where and how it is mined Tin deposits are developed in Southeast Asia, mainly in China, Indonesia, Malaysia and Thailand. Other important deposits are located in South America (Bolivia, Peru, Brazil) and Australia. In Russia, tin ores are mined in the Far East and Yakutia. Deposits in Russia In Russia, there are tin deposits in the North-East, Primorye, Yakutia, and Transbaikalia.

Distinctive features Gray in color, easily changes shape when bent, melting point is about 330 degrees. When bent, it produces a characteristic crunch. Has the property of discarding 2 simple substances. Useful properties Safe, non-toxic, corrosion-resistant coating in pure form or in alloys with other metals. Use in the household Historically, tin found its first use in the form of utensils and weapons. In everyday life it is used for making: various patterns; for various finishing tile options; for applying protective and decorative coatings; for connecting coatings by soldering; for soldering connecting electrical installations.


Deposits in Russia The largest number of deposits of this natural stone is located in the Urals. The source of white marble is the Koelginskoye and Aidirlinskoye deposits, gray marble comes from the Ufaleyskaya and Mramorskaya deposits. Yellow marble is mined in the Oktyabrsky and Pochinsky quarries, black marble is mined at the Pershinsky deposit, pink-red marble is brought from the Nizhne Tagil deposit. There are about 20 deposits of this stone in the Urals, eight of them are under development. Where and how it is mined Marble is mined in quarries using stone-cutting machines equipped with carbide discs, rope... Marble blocks mined in a quarry are transported to a stone processing plant or plant, where they are sawed into slabs of different thicknesses.

Distinctive features Marble has very high mechanical strength. As you know, natural marble is approximately two to two and a half times stronger than concrete and many other types of natural stone. Useful properties For many centuries, marble has been the main material used to decorate buildings, due to its properties such as ductility and strength. Use on the farm Marble flour is used in agriculture.

Image: Symbol: Mineral resource: uranium ore FI: Patokin Oleg

Where and how it is mined Uranium ores are mined in Russia, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Ukraine, Canada, Australia, USA, China, Niger, Namibia. Extraction is carried out by underground borehole leaching. In underground leaching, the preparation, opening and extraction of metals is carried out through wells drilled from the surface. The leaching solution is supplied to injection wells, then the solution is filtered through the ore massif, and the solution with ore is extracted to the surface through a system of pumping wells and transported to a solution processing plant. It is also possible to extract uranium using the mine method. Deposits in Russia The Zherlovoe and Argunskoye deposits are located in the Krasnokamensky district of the Chita region. The reserves of the Zherlovoye deposit amount to 4,137 thousand tons of ore, which contain only 3,485 tons of uranium (average content 0.082%). Uranium reserves at the Argun deposit in category C1 amount to thousands of tons of ore, tons of uranium (average content 0.215%). Reserves in category C2 are: 7990 thousand tons of ore, 9481 tons of uranium (with an average content of 0.12%). Approximately 93% of all Russian uranium is mined here. There are deposits in the Kurgan region and in Buryatia.

Distinctive features Uranium is a very heavy, silvery-white, shiny metal. In its pure form, it is slightly softer than steel, malleable, flexible, and has slight paramagnetic properties. Useful properties Uranium ore is the only source of atomic energy. Economic uses Uranium is used to generate nuclear electricity, nuclear fuel for military and civilian ships and icebreakers, and the manufacture of nuclear weapons. Uranium is used in geology to determine the age of minerals and rocks. Uranium is added in small quantities to glass to give it color. Uranium is a component of various metal alloys and is used in photography and other fields.


Where and how it is mined: in hydrometallurgical quarries - when copper is leached from the rock with a weak solution of sulfuric acid; pyrometallurgical – consists of several stages (concentration, roasting, smelting for matte, purging and refining). Deposits in Russia The largest copper deposit in the world is located in Chile - the Esconida quarry. Other large deposits: mines on the Keweenaw Peninsula (USA, Michigan); Chuquicamata mine in Chile (up to tons per year); the Corocoro mine in Bolivia; Gumishevsky mine (Middle Urals, Russia) – now depleted; valley of the Levikha River (Middle Urals, Russia).

Distinctive features Some copper compounds can be toxic to humans. An increased content of copper in water and food can cause diseases of the liver and gall bladder. Beneficial properties: the bactericidal properties of copper are disproportionately higher. It has been proven that copper helps fight influenza viruses and destroys staphylococci. Household use: Electrical industry (wires). Mechanical engineering. Shipbuilding (hull plating). Construction (pipes, pipelines, roofing and facing materials, bathtubs, faucets, sinks). In art (jewelry, statues, coinage). In everyday life (air conditioners, microwave ovens, coins, food additives, musical instruments). Where and how it is mined Quartz deposits are ubiquitous in nature. Industrial mining of the mineral is carried out in Austria, Brazil, Sri Lanka, Madagascar, and some countries in Europe and Africa. The development of quartz in Russia is carried out in Siberia and the Urals. The mineral is mined from placers, pegmatites and hydrothermal veins. Deposits in Russia In Russia, there is good quartz in the Urals. “Crystal cellars” containing rock crystal, amethyst, topaz and other precious stones are also available in Primorye. Rock crystal is mined in Yakutia. The White Sea amethyst from Cape Korabl is famous. In the Eastern Orenburg region, quartz veins are numerous.

Distinctive features Characteristic features of quartz are a non-metallic luster and high hardness (leaves a scratch on the glass). Quartz can be confused with chalcedony, opal, feldspar and nepheline. Useful properties Quartz has a glassy sheen, sometimes with a greasy tint. The fracture of its crystals is conchoidal or uneven. Quartz dissolves well in hydrofluoric acid. The melting point of the mineral is °C. Due to the strong viscosity of the solution, it is very difficult to determine the exact melting point. Quartz belongs to the group of substances that form glass. Use in the household The scope of quartz is more than wide. Quartz without impurities (rock crystal) is used in frequency generators, sensitive optical devices, and in the creation of microcircuits in radio electronics. This mineral is also used in jewelry, cosmetology and... as a building material (quartz sand, pebbles and crushed stone act as fillers for concrete). Where and how it is mined In ancient times, salt was mined by burning certain plants in fires; the resulting ash was used as a seasoning. To increase the salt yield, they were additionally doused with salty sea water. Deposits in Russia: Artyomovskoye deposit is the largest in Europe. Near the city of Artyomovsk (Donetsk region). Extraction in the mine of the State Production Association "Artemsol" (Soledar). Baskunchak deposit, production from Lake Baskunchak. The Baskunchak railway was built to export salt. Verkhnekamskoye deposit of potassium salts, mine mining by OJSC Uralkali. Iletsk deposit, production in the mine of JSC Iletsksol. Tyretskoye deposit, production in the mine of the Federal State Unitary Enterprise "Tyretsky Salt Mine". Odessa estuaries (mining was carried out from 1774 to 1931). Elton field. Seryogovskoe deposit (evaporation of brine).

Distinctive features Table salt is used industrially to produce soda, chlorine, hydrochloric acid, sodium hydroxide and sodium metal. Beneficial properties Acids are opposed by a group of substances called bases. (Strong bases are called alkalis.) These substances have a bitter taste, are chemically active, change the colors of dyes, but to the opposite ones compared to acids, etc. Solutions of acids neutralize solutions of bases. In other words, a mixture of acid and base, taken in a certain ratio, exhibits the properties of neither acid nor base. This mixture is a solution of a salt, which is usually much less chemically active than an acid or base. Thus, when mixing appropriate quantities of solutions of a strong and caustic acid (hydrochloric acid) with a strong and caustic alkali (sodium hydroxide), a solution of sodium chloride, i.e., ordinary table salt, is obtained. Household use In cooking, salt is used as an important seasoning. Salt has a characteristic taste that is well known to every person, without which food seems bland. This feature of salt is due to human physiology, but people often consume more salt than is necessary for physiological processes. Salt has weak antiseptic properties; % salt content prevents the development of putrefactive bacteria, which is the reason for its widespread use as a preservative for food and other organic matter (leather, wood, glue). Now there are many exotic varieties of salt (smoked French, pink Peruvian, Himalayan rock pink is mined by hand in the Himalayas, mainly in Pakistan, etc.), in some restaurants (for example, in the Thai resort of Phuket) there is even a specialty “salt sommelier”. Deposits in Russia Oil production is carried out in Eastern Siberia: Krasnoyarsk Territory, Republic of Sakha (Yakutia), Irkutsk Region. The Tuymazinsky oil field is located in the Republic of Bashkiria, near the city of Tuymazy, and was discovered back in 1937. The Yety-Purovskoye oil field is located in the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug, near the city of Noyabrsk. Discovered in 1982, development began only in Oil reserves amount to about 40 million tons. The Samotlor oil field (Samotlor) is the largest oil field in Russia and one of the largest oil fields in the world, located in the Khanty-Mansiysk Autonomous Okrug, in the Nizhnevartovsk region near Lake Samotlor. Verkh-Tarskoye oil field. Located in the north of the Novosibirsk region. Oil reserves amount to about 68 million tons. Where and how it is produced Oil, along with natural gas, accumulates in porous rocks called reservoirs. They may be different. A good reservoir is considered to be a layer of sandstone, which is located between layers of clay and shale. This eliminates the leakage of oil and gas from underground reservoirs: extracted through drilling wells

Distinctive features Oil is a dark-colored oily liquid with a characteristic odor. The aroma of oil is given by the accompanying hydrogen sulfide and the remains of plant and animal organisms. Each oil has its own unique color: dark green oil of the Caucasus, yellowish oil of Siberia, pinkish oil of Belarus, absolutely black oil of Mangyshlak. Beneficial properties The beneficial properties of oil have been known to man since ancient times. “Stone oil” was widely used in construction in ancient times. In Egypt and between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, buildings erected 3 thousand years BC have been found. structures whose wall and floor slabs were held together with oil. The walls of granaries and reservoirs were covered with bitumen. Oil was added to embalming compounds in ancient Egypt. In the Middle Ages, it was mixed into drying oil to improve paints. Oil was actively used in medicine, and, by the way, not only by the ancients. Back in the mid-19th century in the United States, refined oil called “Seneca oil” or “mountain oil” was offered as a remedy for headaches and toothaches, deafness, rheumatism, dropsy, and was recommended for healing wounds on the backs of horses and mules. Naturally, oil was also used for lighting in ancient times. Household Use Oil is not only the main component of fuel for cars and jet aircraft. The products obtained from oil refining help create items that are used every day by people around the world, such as polyethylene plastic, which is used to make food containers, plastic bags and other products. For many years, humanity has used natural cosmetics for the lips, eyes and face, but most of the eyeliners and lipsticks on the market today gain all their beauty from petroleum products and petroleum products, such as propylene glycol. Many modern girls wear nylon tights. In addition to the above, solar panels, wrinkle-resistant clothing, chewing gum, colored paraffin pencils, aspirin and many other useful things are made using oil.

Our land is great and rich in various minerals!
In schools, from the very beginning of studying a subject such as geography, children are explained what wealth is extracted from the bowels of the earth. Children will learn in which part of the world certain natural resources can be found. A map with mineral symbols helps them with this.
The riches of our land
On a geographical map, topographers apply special symbols and signs indicating what exactly is located in a particular place. For example, forests are indicated as trees or in the form of a green rectangle, seas - in the form of a blue rectangle, sandy terrain - in yellow, and so on.
The earth is rich in such minerals as oil, gas, coal, peat, black ore, non-ferrous ore, lime, clay, sand, granite, precious stones (ruby, diamond, sapphire, emerald), fresh water, mineral water and so on. Thanks to topographers, people find out in which area gas or oil is produced, and much more.
According to the designations of mineral resources on the map of Russia, it is rich in oil and gas (Tyumen, Tomsk, Novosibirsk, Perm, Orenburg regions, the Republic of Tatarstan, Bashkortostan and so on), coal (Pechora, Kuznetsk, South Yakutsk basins), oil shale (St. -Petersburg deposit), peat (Northern Urals, Western Siberia), iron ores (Kursk), copper (Norilsk) and much more.
Students learn how minerals are mined, how they are cultivated, and how they need to be protected.
Symbols of mineral resources on the map
Each fossil has its own designation. Let's look at the most common ones:
- Coal is designated in the shape of a black square. Brown coal is a white square with diagonal black stripes. Oil shale is a black parallelogram. Oil is a black elongated trapezoid, similar to a triangle. Gas is the same symbol as oil, only white. Iron ore is a black triangle. Aluminum ores - a white circle inside a black square. Copper - black rectangle. Gold is a black and white circle, colored in half. Table salt - white cube.

Knowing what a particular symbol means, you can easily decipher any card.
Our land is great and rich in various minerals!
In schools, from the very beginning of studying a subject such as geography, children are explained what wealth is extracted from the bowels of the earth. Children will learn in which part of the world certain natural resources can be found. A map with mineral symbols helps them with this.
The riches of our land
On a geographical map, topographers apply special symbols and signs indicating what exactly is located in a particular place. For example, forests are indicated as trees or in the form of a green rectangle, seas - in the form of a blue rectangle, sandy terrain - in yellow, and so on.
The earth is rich in such minerals as oil, gas, coal, peat, black ore, non-ferrous ore, lime, clay, sand, granite, precious stones (ruby, diamond, sapphire, emerald), fresh water, mineral water and so on. Thanks to topographers, people find out in which area gas or oil is produced, and much more.
According to the designations of mineral resources on the map of Russia, it is rich in oil and gas (Tyumen, Tomsk, Novosibirsk, Perm, Orenburg regions, the Republic of Tatarstan, Bashkortostan and so on), coal (Pechora, Kuznetsk, South Yakutsk basins), oil shale (St. -Petersburg deposit), peat (Northern Urals, Western Siberia), iron ores (Kursk), copper (Norilsk) and much more.
Students learn how minerals are mined, how they are cultivated, and how they need to be protected.
Symbols of mineral resources on the map
Each fossil has its own designation. Let's look at the most common ones:
- Coal is designated in the shape of a black square.
- Brown coal is a white square with diagonal black stripes.
- Oil shale - black parallelogram.
- Oil is a black elongated trapezoid, similar to a triangle.
- Gas is the same symbol as oil, only white.
- Iron ore - black triangle.
- Aluminum ores - a white circle inside a black square.
- Copper - black rectangle.
- Gold is a black and white circle, colored in half.
- Table salt - white cube.