High voltage coil. The principle of operation of the ignition coil. Its types and device
It is used as a high-voltage step-up transformer - storage el. energy in the inductance, to create an arc discharge on the electrodes of the spark plug, lasting 1-3 ms.
PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION
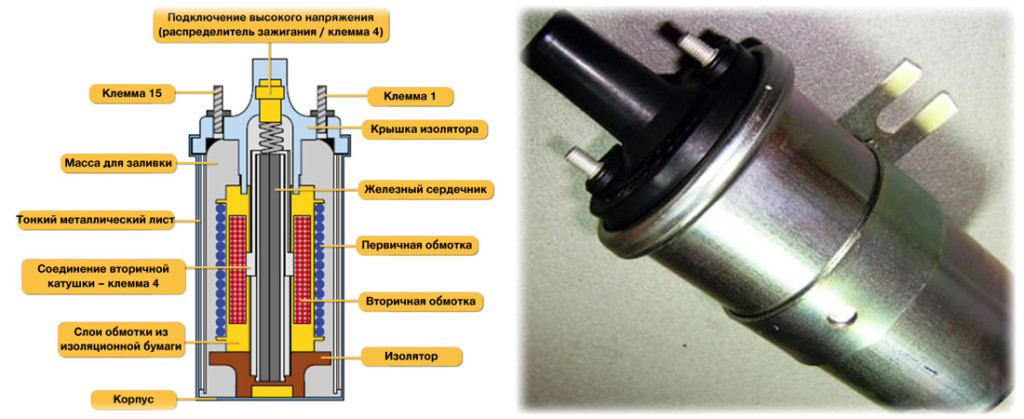
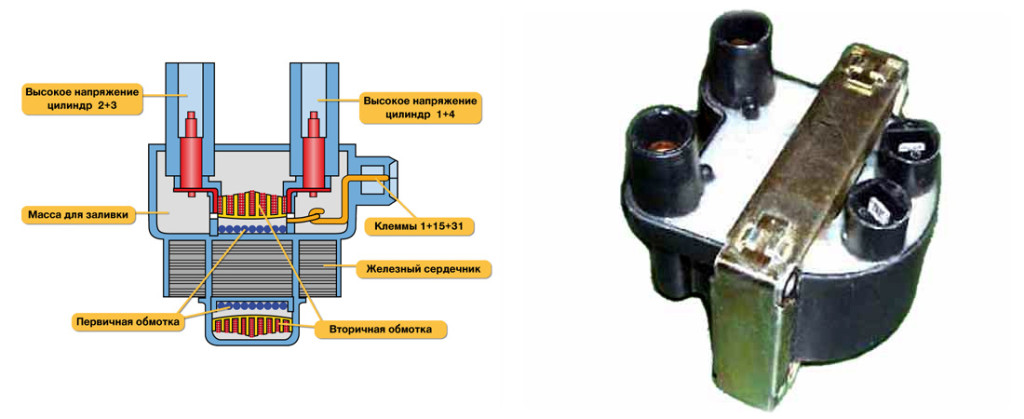
Rice. Sectional ignition coil: 1 - insulator; 2 - case, 3 - insulating paper, 4 - primary winding, 5 - secondary winding, 6 - primary winding output terminal (designations: "1", "-", "K"), 7 - contact screw, 8 - central terminal high voltage, 9 - cover, 10 - power terminal (designations: "+B", "B", "+", "15"), 11 - contact spring, 12 - bracket, 13 - outer wire, 14 - core.
The figure shows a sectional view of the ignition coil and one of the winding connection diagrams. Let's repeat what we said earlier: coil- a transformer with two windings wound on a special core.
First, the secondary winding is wound with a thin wire and a large number of turns, and the primary winding is wound on top of it with a thick wire and a small number of turns. When the contacts are closed (or in another way), the primary current gradually increases and reaches the maximum value determined by the voltage battery and ohmic resistance of the primary winding. The rising current of the primary winding meets the resistance of the emf. self-induction directed opposite to the battery voltage.
When the contacts are closed, a current flows through the primary winding and creates a magnetic field in it, which also crosses the secondary winding and a high voltage current is induced in it. At the moment of opening the contacts of the breaker, both in the primary and in the secondary windings, emf is induced. self-induction. According to the law of induction, the higher the secondary voltage, the faster the magnetic flux created by the magnetic current of the primary winding disappears, the greater the ratio of the number of turns, and the greater the primary current at the moment of rupture.
This design is typical when building ignition systems using breaker contacts. The ferromagnetic core can be saturated with primary current, which would lead to a decrease in the energy accumulated in the magnetic field. To reduce saturation, an open magnetic circuit is used. This allows you to create ignition coils with a primary winding inductance of up to 10 mH and a primary current of 3-4 A. Higher current cannot be used because at this current, burning of the breaker contacts may begin.
If the inductance in the coil is Lk = 10 mH and the current I = 4 A, then the energy W of no more than 40 mJ can be stored in the coil at efficiency = 50% (W = Lk * I * I / 2). At a certain value of the secondary voltage, an electrical discharge occurs between the electrodes of the spark plug. Due to the increase in current in the secondary circuit, the secondary voltage drops sharply to the so-called arc voltage, which supports the arc discharge. The arc voltage remains almost constant until the energy reserve becomes less than a certain minimum value. The average duration of battery ignition is 1.4 ms. This is usually sufficient to ignite the air-fuel mixture. After that, the arc disappears; and the residual energy is spent on maintaining damped voltage and current oscillations. The duration of the arc discharge depends on the amount of stored energy, composition of the mixture, crankshaft speed, compression ratio, etc. With an increase in the crankshaft speed, the time of the closed state of the breaker contacts decreases and the primary current does not have time to increase to the maximum value. Because of this, the energy stored in the magnetic system of the ignition coil decreases and the secondary voltage decreases.
The negative properties of ignition systems with mechanical contacts appear at very low and high crankshaft speeds. At low speeds, an arc discharge occurs between the breaker contacts, which absorbs part of the energy, and at high speeds, the secondary voltage decreases due to the “bounce” of the breaker contacts. Contact systems have not been used abroad for a long time. Cars made in the 80s are still roaming our roads.
Some ignition coils work with an additional resistor. A functional diagram of the connection of such a coil with a contact ignition system is shown nearby.
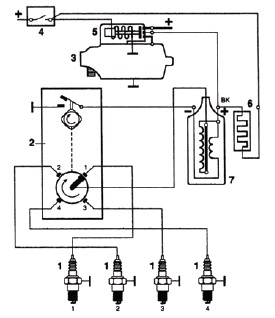
Rice. Connection diagram of the ignition coil with a contact ignition system: 1 - spark plugs, 2 - distributor, 3 - starter, 4 - ignition switch, 5 - starter solenoid relay, 6 - additional resistance, 7 - ignition coil.
The connection scheme of the coil windings is different. In starting modes, when the voltage on the battery drops, the additional resistor is short-circuited by the auxiliary contacts of the starter retractor relay or the contacts of the additional starter enable relay, which provides the primary winding of the ignition coil with an operating voltage of 7-8 V. In engine operating modes, the supply voltage is 12-14 V. An additional resistor is usually wound from constantan or nickel wire. If the wire is nickel, then such a resistance is called a variator due to the change in resistance from the amount of current flowing through it: the greater the current, the higher the heating temperature and the higher the resistance. At increased crankshaft speeds, the primary current drops, the heating of the variator weakens and its resistance decreases. Tzh. Since the secondary voltage depends on the breaking current in the primary circuit, the use of a variator makes it possible to reduce the secondary voltage at low and increase it at a high engine crankshaft speed.
In transistorized ignition systems, the primary current is interrupted by a power transistor. In such systems, the primary current is increased to 10 - 11 A. Ignition coils are used with a low resistance of the primary winding and high coefficient transformations. Here are samples of oscillograms taken in a working system on the primary and secondary windings of the ignition coil.
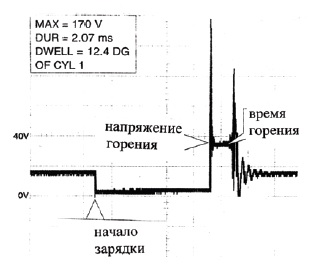
Rice. Oscillogram of the primary winding.
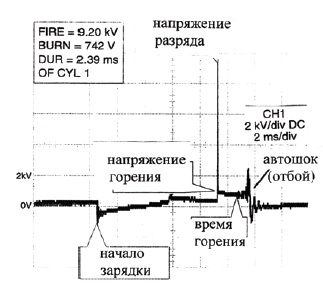
Rice. Oscillogram of the secondary winding.
The shape of the oscillograms is very similar, because the windings of the coil are interconnected by a transformer connection (mutual induction). Coils of contact-transistor and transistor ignition systems have a classic design: oil-filled, with an open magnetic circuit, in a metal case. Let's give some data on produced domestic ignition coils.

As water from the table, the ignition coils differ in the number of turns in the windings and the transformation ratio in various ignition systems. The designs of the coils differed little.
LOCATION
Under the hood on the fender or on the dividing panel between the engine compartment and the vehicle interior. Sometimes directly on the engine.
FAULTS
The main fault is a break in the primary or secondary windings. Sometimes the oil pressure relief valve is triggered by overheating. After draining the oil, the coil fails. Some coils continue to work even with a break in the secondary winding, while throttling gaps are observed.
During long-term operation of the vehicle, the insulating properties of the materials used in the ignition coils lose their properties and high-voltage burnouts occur, allowing part of the charge to “leave” to ground. When inspecting the ignition coil, such a malfunction is easily detected by a gray mark on the surface of the coil insulator (similar to a trace from simple pencil) or burnout blackness with a partially charred surface.
It is necessary to inspect the BB connector of the wire coming out of the ignition coil. In 70% of cases there is an oxidized surface or rust. In this case, be sure to check the central BB wire. Its resistance should be no more than 20 kOhm. A common situation: the BB wire rings, the resistance is up to 20 kOhm, and the combustion oscillogram on all cylinders is equally wrong. With a sharp throttling, the combustion oscillogram is even more distorted, chaotic sparking is observed, and only the replacement of the central explosive wire brings a positive result.
Job gasoline engine Internal combustion is possible only if there is a spark in the combustion chamber. The spark must be given in time and be strong enough to ignite the air-fuel mixture. The ignition system of the car is responsible for this process. It consists of many elements and the ignition coil plays a very important role in the system.
It is very difficult for an electric spark to form in the conditions of a dielectric medium created by fuel-air mixture in the combustion chamber. The smallest electrical breakdown under such conditions is possible only in the presence of a very high voltage. An electrical impulse of such strength simply cannot occur at a voltage of 12 volts, which the car's on-board power supply system has. The voltage that can cause a short-term spark on the spark plug electrodes must be at least tens of thousands of volts.
To create a pulse of such a high voltage, an ignition coil is used. It is designed to convert voltage onboard system electrical equipment at 6, 12 or 24 volts in a short-term impulse with a voltage of up to 30,000 volts. The device transmits an impulse to a candle, where a spark occurs between its contacts, which is necessary for the working mixture to ignite.
Ignition coils of one configuration or another are installed on all internal combustion engines, without exception, running on gasoline or gas. It is used on all types of ignition systems without exception - contact, non-contact and electronic.

Fundamentally, the ignition coil is very simple. It has two windings - primary and secondary. A wire with a large cross section creates the primary winding, and the secondary is wound with a thinner wire and the number of turns can be up to 30,000. The primary winding has about a hundred turns. The windings are located around a metal rod - the secondary winding is below, and the primary winding is wound on top of it.
Both windings, like the core, are enclosed inside a dielectric case, inside which is transformer oil. The whole assembly is a step-up transformer. A low voltage current is applied to its primary winding, and a high-voltage pulse is removed from the secondary.
Types of coils and their connection diagrams

With absolutely the same design, the coils are connected according to different schemes that determine the type of device:
- common coil;
- individual coil;
- double or double ended.
The simplest and oldest type of coils. Its connection scheme assumes the presence of only one coil, which transmits a high-voltage pulse to a switchgear - a distributor. It already distributes high voltage between the candles of the cylinders, according to the order of their work. This connection scheme can be used on ignition systems of all existing types– electronic, contact and non-contact.
The functioning of the bobbin is based on the process of electromagnetic induction - a high-voltage impulse occurs when small currents pass through the primary winding, exciting a magnetic field in the high-voltage winding, which causes a powerful impulse that enters the candles.
Individual type coil
Electronic ignition systems can only work with these coils. They differ in the connection scheme and in appearance - each candle has its own coil and this contributes to much better synchronization of the gas distribution phases with the moment of ignition of the mixture of gasoline and air.
![]()
Coils of individual design are dry and have electronic parts of the igniter in their design. The windings are arranged in reverse order, and the current of the secondary winding goes straight to the contacts of the candle. The design of these coils assumes the presence of a diode that cuts off high currents.
Dual ignition coils
Purpose of the ignition coil
The ignition coil is one of the most important elements for igniting the fuel in the engine cylinders. It is a device that consumes low-voltage current from a car battery and converts it into high-voltage pulses. They at the right time form a spark between the electrodes of the spark plug and ignite the fuel-air mixture.
Design
The device of the ignition coil is similar to a transformer: it also has two windings (primary and secondary) on the core, and a special device converts the direct current of the battery into a pulsed one, the voltage of which rises several thousand times according to the law of electromagnetic induction. In the ignition systems of older cars, there was only one such node. Pulses from it were alternately applied to all the candles through the distributor and high-voltage wires. But in Lately on machines, a system with the removal of a separate coil for each cylinder is increasingly common.
Diagnosis by closing the spark plug to the body
Without this device, the car is not able to start. Therefore, checking the ignition coil is the operation that any motorist should be able to perform. The most common way is to unscrew the spark plugs from the cylinder and short them to the engine case and then try to start the car. If a spark jumps between the electrodes, then the ignition coil is working. If not, then most likely the problem is in this device. But many motorists have an opinion that with this method of checking, the ignition coil can be damaged.
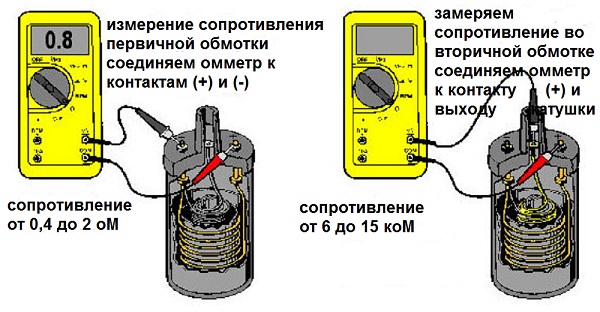
Diagnosis by resistance measurement

There is a safe alternative, but in this case you will need an ohmmeter. The method consists in measuring the resistance of the windings. Their exact values \u200b\u200bare indicated in technical reference books, but usually a working ignition coil has a resistance of 16-17 KΩ on the primary winding. If a strong discrepancy with this figure is found, or even a break (infinite resistance) or a short circuit (the value will tend to zero), then most likely this unit is faulty.
Alternative diagnostic methods
Another way is to install your reel on another machine. In this case, you will definitely know if this component is working. The difficulty is that the car must be the same brand and the same configuration as yours, and you also need the consent of its owner. There are also visual signs of coil failure: the smell of burnt insulation or traces of breakdown (the presence of black burnt points on the body and windings).
Is it possible to repair the ignition coil
What to do if a malfunction of this component of the ignition system is established? Only change - the coil cannot be repaired. More precisely, it can be repaired, but the complexity of replacing the windings makes such an operation unprofitable. 
Work methodology
Remember safety precautions for all manipulations with the ignition system, since the coil voltage can reach 20-25 thousand volts. Use tools with electrically insulated handles and do not work in damp areas or in the rain. If you cannot find the cause of the car malfunction on your own, contact a specialized service. Good luck on the roads!
The ignition coil is the second element in the sequence of the car engine ignition system. The operation of the ignition coil is similar to the functions of a transformer and is based on the conversion of low voltage from the vehicle's battery (starter) battery into high voltage generated for spark plugs, as a result of which the air-fuel mixture is ignited.
The coil consists of primary and secondary windings, an iron core and a housing with insulation. On the core, recruited from thin metal plates, two windings of thick and thin copper wire are wound.
The principle of operation of the ignition coil is similar to that of a transformer. When voltage is applied to the primary circuit, a magnetic field is created in the coil. The secondary winding of the ignition coil is self-induced and generates a voltage. The transformed voltage is applied to the spark plugs through the switchgear, and the high voltage discharge continues until the energy created by the coil is used up.
Varieties of coils
To date, there are a sufficient number of types of ignition coils that can be installed both on old domestic cars with carburetor engines, and on more modern cars with direct fuel injection.

Housing ignition coils are installed on vehicles with mechanical ignition distribution, where the distributor, rotating, supplies high voltage to each spark plug in a certain sequence. This method of switching and voltage distribution is not used in modern automotive industry due to short service life and low reliability.
A coil with electronic ignition distribution, or a distribution coil, does not require an additional contact cascade interrupter for its operation, because with the development of technologies in microelectronics, it has become possible to integrate such an ignition interrupter into the coil itself. This coil is suitable for cars with mechanical ignition distribution.
The dual-spark ignition coil allows the voltage to be generated for the spark plugs simultaneously in two engine cylinders per revolution of the crankshaft, while coordination between the ignition system and the camshaft is not required. It is advisable to use such coils only in engines with an even number of cylinders, for example, for an engine with four cylinders, you will need two coils, with six - three, respectively, with eight - four.

The "intelligent" plug-in ignition coil is single spark and is mounted directly on each spark plug. The design and functional characteristics of such a coil make it possible to abandon the use of high-voltage wires in the system, but at the same time, connecting clamps (terminals) designed for high voltage are required. Due to their compactness, these coils are used in cars with a small amount of free engine compartment space, but compact does not mean inefficient. The plug coil can easily compete with its counterparts.

The advantages of the coil are:
- The widest range of ignition timing settings.
- Diagnosis of misfires from the primary and secondary windings.
- Spark suppression in the secondary circuit using a high-voltage diode.
Such devices are used for engines with any number of cylinders, however, synchronization with the position of the camshaft using an appropriate sensor is strictly required here.
Coil malfunctions and their diagnostics
The ignition coil is a fairly reliable element of the system, but all sorts of malfunctions, often associated with non-compliance with the operating rules, do not bypass it. Consider the most common signs of a malfunctioning ignition coil:
- Unstable engine speed at idle.
- Engine failures with a sharp opening of the throttle.
- The check fired up.
- There is no spark.
First of all, in the event of a breakdown in the ignition system, you should visually inspect the coil and find cracks, charring, as well as check its temperature and humidity. If the ignition coil is heated, then this may indicate that an interturn circuit has occurred and the device must be replaced. High humidity in the place where the ignition coil is located can also affect the operation of the engine. If the coil is dry, without cracks, soot and not hot, but there is still a malfunction in the system, it is necessary to diagnose it.
If the car does not start, that is, the starter rotates, but the engine does not pick up the ignition, this may mean that there is no spark from the ignition coil.
- How to test the ignition coil for operability for a contactless ignition distribution system? It is necessary to disconnect the high-voltage wire located in the center of the ignition distributor and place this wire at a distance of about 5 millimeters from the metal case of the engine. Then we scroll the engine crankshaft with the starter and observe the presence of a spark in the gap between the contact part of the high-voltage wire, which was disconnected from the distributor, and the engine housing (ground).
- In a contact ignition system, this procedure excludes crankshaft cranking by a starter, namely: remove the cover of the ignition distributor and set the contacts of the voltage breaker to the closed state. Then we turn on the ignition with the breaker lever, open and close the contacts. The presence of a spark in the gap between the wire and the ground tells us about the correct operation of the ignition coil.

If the diagnostics of the ignition coil revealed the absence of a spark, then you need to check the resistance of the ignition coil. To do this, you need a conventional multimeter, or an ohmmeter and technical certificate on the coil, where you can see its parameters, including the resistance of the windings. Before checking the ignition coil, disconnect all the wires and measure the resistance of both windings one by one, while the resistance of the primary winding should be less than that of the secondary. If during the measurements it turned out that the resistance of both windings corresponded to the factory parameters, and when checking “for a spark” there was no such spark, then we can conclude that there was a breakdown of the insulation between the turns and the case.
Replacing the ignition coil
If the coil fails and cannot be repaired, it must be replaced. You can buy exactly the same original one, or you can pick up a similar one, while their characteristics should not differ by more than 20-30 percent, as well as have the same mounting and design. For example, for domestic cars VAZ-2108 - 2109 with electronic coils 27.3705 from a domestic manufacturer, the Bosch coil 0.221.122.022, which is not very different in parameters, will do. In this case, the spread of parameters will be from 10 to 15%.
Summing up, it can be noted that when writing the article, real information was used about the problems that each driver faced. All coils practically do not differ from each other in terms of the principle of operation, but not all of them are interchangeable, for example, coils with mechanical ignition distribution will not be able to work with contactless distribution and vice versa.
Regardless of the engine management system, working principle of the ignition coil remains unchanged. The functional purpose in the coil ignition device is to convert the low-voltage on-board current coming from the car battery into high-voltage.
The function of the coil is constant for all ignition systems that are this moment So far, only three have been developed:
- with contact control;
- with electronic control;
- with contactless control.
In the classification of automotive equipment, three types of high voltage coils:
- with individual design;
- with a double body;
- general execution.

Coil of individual design type
This type of coils is installed together with ignition, the operation of which is fully electronically controlled and with no mechanical parts. Such a system is usually called direct, since the ignition is produced by means of a discharge from a capacitor.
The design of such a system provides for the installation of the coil body directly on the candle, hence the name of this type of coils.
Main functional part The coil consists of turns of copper wire for the primary voltage reception and secondary conversion circuit. Distinctive feature is the location of the primary winding inside the secondary converter. The first circuit includes an internal core in the primary winding, and the secondary circuit in the form of an outer casing goes around the secondary winding.
An igniter capacitor is enclosed under the casing of the coil body of an individual design. The high-voltage current generated in the secondary winding is supplied to the contact of the candle, on the contact of which the coil is installed.
To do this, a special tip was introduced into the design, consisting of a rod that is in direct contact with the candle, a pressure spring and an insulator. The current is cut off by a diode.





