Mix mineral and synthetic gear oil. What to do with a possible mixture of gear oils? What is known about the composition
Although many transmission fluids have similar characteristics, their bases differ, as does the set of active chemical additives and process impurities. Different transmission fluids also react differently to changing weather and temperature conditions. That is why service stations do not recommend mixing transmission oil fluids even with similar technical characteristics.
Some power steering systems are designed to work with automatic transmission fluid, which is a red coloring fluid pink color. In other cases, the standard mineral oil for hydraulic systems, which is suitable for various hydraulic steering systems, as it meets the requirements of several brands. In any case, each steering system uses a different oil that can keep the pump and steering gear well lubricated, protect them from corrosion, and keep the steering system running smoothly in every situation.
What are transmission oils?
All gear oils are made on three modern types of bases: synthetic, mineral and semi-synthetic. Oils differ in the degree of viscosity, which is divided into 3 subgroups defined by the SAE classification:
- For winter use indexes 70-85W are characteristic
- For summer use- indices 80-250W
- all-weather (universal) indices - 75-90W and 80-140W
There is also an API classification system that divides oils into 7 subgroups from GL1 to PD-6, as well as MT-1, depending on the degree of permissible load on the gear lubricant.
Power steering duty cycle. The main feature of power steering oil is to be incompressible, that is, after the pressure generated by the pump, the oil will transfer all that pressure directly to steering.
When the pump starts to work, the oil contained in the reservoir is sucked in, the oil inside the pump is compressed, but at the same time, its lubricity helps the pump maintain a long service life by reducing internal friction, hence wear and tear, excessive temperature.
Although gear lubricants may have similar viscosity index or load index values, there are still significant differences between them in terms of the chemical additives they contain. It is these additives that do not allow mixing gear oils, because. each manufacturer independently develops their composition and set, which are a trade secret of each brand.
After compression, the oil flows into the steering box through the sealed hoses of the system. Oil enters the steering mechanism and pushes the piston, providing hydraulic assistance. Meanwhile, the oil on the other side of the piston flows into the reservoir and thus maintains the oil level within the specified range.
The friction of the internal components of the pump and steering gear generates heat which is transferred to the oil, this is also subjected to system pressure, hence the oil temperature increases as the load on the steering system increases. The oil undergoes a slight dilatation perceived through the reservoir as the oil level inside it increases. However, if the system is supplied with the correct amount of oil, this increase does not change the operation of the system.
The only situation that allows mixing gear oils, is an emergency loss of the volume of the oily liquid, because severe lack of oil level in the transmission is much worse than possible mixing. It should be borne in mind that this is a temporary measure and at the first opportunity it is necessary to replace the transmission mixture.
This little primer shows the color of the oil during its lifetime. The darker coloration when it reaches the end of its cycle is due to air contact, oxidation, system fouling due to small leaks and metal fragments from the moving parts of the pump and steering gear.
At the beginning of the article, the oil used in the power steering system is often ignored by owners and technicians, and this is due to the fact that it works in a hostile environment. There are no significant thermochemical reactions inside the hydraulic steering system, so there are also no excessively high temperatures and pressures, so there is little oil change during its operation. Thus, some car brands simply recommend an exchange only if the system fails.
What does mixing gear oils do?
There are no aggressive modes in the transmission units, as, for example, in the engine, so some car owners resort to mixing transmission oils when it becomes necessary to normalize the fluid level in the box. However, due to their different composition, when mixing transmission fluids, a negative effect may appear. chemical reaction, which leads to the appearance of white flakes of sediment, which clogs the entire transmission system. This problem is especially relevant for owners of cars with automatic transmissions and CVTs. As a result, the gearbox can completely fail, and the components and parts of the transmission will receive significant damage.
Time, direction and conditions of vehicle use are sufficient factors to avoid obtaining an accurate estimate of when power steering oil should be replaced by oxidation or complete loss of performance. When using the vehicle, both the pump and the steering wheel release metal fragments that are charged with oil. They, as they increase their concentration in the oil, can wear out the steering cylinder and hydraulic pump chamber if they reach it.
What to do with a possible mixture of gear oils?
If for some reason a mixture of gear oils has occurred, and you notice the appearance of failures in the operation of the gearbox, it is necessary to carry out a complete oil change as soon as possible using special flushing agents. Since it is necessary to carry out a complete fluid change, it is better to contact a car service, because. it is difficult to perform this procedure on your own. After that, fill in the gear lubricant recommended by your vehicle manufacturer.
In addition, the oil itself has its attributes weakened with time of use, causing steering system components to be more susceptible to corrosion, oxidation causing it to lose its ability to withstand system temperatures until the oil changes color when it is worn.
Power steering oil change is most often done when a system component is replaced. In this process, you need to open the system to replace the defective component with a new one. Therefore, many brands recommend changing the oil from the power steering system under the threat of voiding the warranty, otherwise. The reason is to avoid that contaminants contained in old oils damage mainly the steering gear and pump.
It is necessary to choose gear oil strictly according to the recommendations of the automaker. In addition, we recommend that you purchase only products from well-known, experienced manufacturers of motorists. In the IXORA store you will find a wide range of original quality gear oils for any make and model of car.
Power steering oil change. The indication of the oil level inside the reservoir can be in the lid itself or written in high relief on the reservoir body. The old oil must be drained from the reservoir, so the hoses are disconnected from the reservoir and the oil is drained. The hose that is attached to the pump is connected to the reservoir and filled with new oil. The goal is to use this oil to push out old oil contained in other system components.
To do this, the return hose connecting the steering to the tank is routed into a container. Thus, you turn the steering wheel from side to side, avoiding hitting the stops that limit the rotation of the steering wheel. Oil will be sucked from the reservoir and pushed into the steering box. The oil leaving the casing return pipe flows into the aforementioned vessel.
| Manufacturer | Detail number | Part name |
|---|---|---|
| FEBI | 21829 | Transmission oil Febi SAE EU, 75W, synthetic, 1L |
| HYUNDAI | 0430000140 | Transmission oil Hyundai KR, 75W-85, semi-synthetic, 1 |
| TOTAL | 166277 | Transmission oil Total Total Transmission Bv Gl-4, 75W-80, transmission, 1L |
| VAG | G052171A2 | Transmission fluid VW G052 171 EU, synthetic, 1L |
| TOYOTA | 0888581001 | Transmission fluid Toyota LV MT Gear Oil UAE, 75W, mineral, 1L |
| HONDA | 0826199964 | Transmission oil Honda Ultra KR-III JP, KR-III, mineral, 4L |
| HYUNDAI | 0430000110 | Transmission oil Hyundai KR, 75W-85, semi-synthetic, 1L |
| CASTROL | 4671920060 | Transmission oil Castrol Syntrax Universal Semi-Synthetic EU, 75W-90, semi-synthetic, 1L |
| MOBIL | 142123 | Gear oil Mobil Gl-45 Mobilube SHC, 75W-90, synthetic, 1L |
| CASTROL | 4671880060 | Transmission oil Castrol syntrans Transaxle Gl-45 Synthetic, 75W-90, synthetic, 1L |
| ENEOS | OIL1300 | Transmission fluid Eneos ATF Dexron ii JP, Dexron-II, mineral, 1L |
| TOYOTA | 0888680506 | Transmission fluid Toyota ATF Mineral EU, Dexron-III, mineral, 1L |
| MITSUBISHI | ACH1ZC1X05 | Transmission fluid Mitsubishi Diaqueen ATF SP-III US A, mineral, 1L |
| ENEOS | OIL1304 | Transmission fluid Eneos ATF Dexron ii JP, Dexron-II, mineral, 4L |
| HYUNDAI | 0450000400 |
Today we’ll talk with you about whether it is possible to mix gear oils from different manufacturers, and what will happen if they are accidentally or deliberately mixed? In many ways, the situation with transmission lubricant is the same as with engine oils.
Both that, and another to the full is not the unified product. That is, roughly speaking, according to the rules, despite similar characteristics, transmission lubricants differ and experts do not recommend mixing them (or doing this in the most extreme cases).
As the pump draws oil from the reservoir, the reservoir level drops, but under no circumstances does the reservoir dry out completely. Otherwise, the system will be polluted with air. When new oil begins to flow out of the return hose, the return hose must be connected back to the reservoir. Fill the tank up to maximum level, but never exceed this level, as oil expansion must be taken into account, which, when it occurs, increases the volume.
If air enters the system, the pump will begin to make noise at low engine speeds and when the steering wheel is level, indicating the presence of air in the pump. As a vehicle owner, it is important to be very careful and be well informed about the fluid you are using in your transmission. Therefore, today we will inform you about the different types of transmission fluids used in classic, modern and automatic boxes gears.
Can gear oils be mixed? different manufacturers, an analysis of the components of these lubricants themselves will prompt. So, what is gear oil made of?
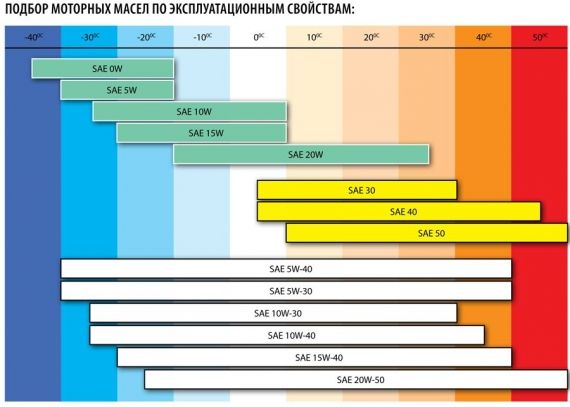
What is known about the composition?
Modern any transmission oil, as a rule, consists of basic foundation on which this type of oil is based: synthetics, semi-synthetics, minerals. So the base of oils from different manufacturers may be the same (well, or almost the same). The other part of the lubricants is made up of certain additives and additives characteristic of a given manufacturer. It is they who betray their own, unique difference to the transmission oil.
They are different for different companies - they differ and constitute, for example, a source of pride for the developer. Formulas of additives and additives are sometimes kept in the deepest secret and protected by trade secret laws (I immediately remember what industrial espionage is)! Like engine oils, transmission oils have different tolerances, temperature conditions for successful operation, additives and additives. So, the driver who is going to add some oil to the transmission needs to remember this, first of all.
Transmission fluid is designed for the transmission system, whether automatic or manual, as water is designed for an aquarium. Some people spend hundreds of dollars on their tropical fish hobby. The same rule applies to vehicles. A car is a great investment. The transmission fluid is used in the transmission as a lubricant to provide the transmission with a way to dissipate excess heat and act as a power emitter by using hydraulic pressure to move valves and apply belts and clutches.

What happens if you mix?
Of course, in the transmission unit such temperature regimes as in the engine itself are not observed, you say. Therefore, why not add an analogue from another company, because there is nothing military in this? And you will be absolutely wrong. When mixed, precipitation in the form of whitish flakes is possible.
What is the risk? They can clog the entire transmission system (especially suffer in this case). Filters can also be clogged, and then the entire system will fail rather quickly. And who needs such a risk? Of course, there are options that will carry over, and the sediment may not form. But is it worth playing such a lottery, where the health and normal functioning of such an important unit as the transmission unit is at stake?
There are many on the market different types transmission fluids. chemicals and solids designed to provide the best absolute lubricity and yet allow slip-free handling of belts and couplings. Transmission fluid is usually dyed red or green. This is to prevent accidental use of the wrong fluid, such as engine oil. Some transmissions use a dipstick to help you correctly gauge the amount of transmission fluid.

One of the popular misconceptions
Lubricant for transmission, as well as motor, is divided into three varieties: mineral water, synthetics and semi-synthetics. Even among experienced drivers, there is a certain misconception that if synthetics are added to a mineral water, a semi-synthetic mix will come out (regardless of production). And that in this way it is possible to mix almost any oil. But this is far from true. Better and we won't check on personal experience and listen to the experts.
With such mixing, the formation of foam is observed, and after about 500-700 km. precipitation appears in the form of the same whitish flakes. And then, somewhere in the 1000 kilometers traveled, the slurry also begins to thicken, clogging all possible holes and the entire system.
Others use a visible hole, similar to how you would like to check the fluid level in a manual transmission. However, others are completely closed and there is no way to know if the fluid level is correct unless you use a sensor to send fluid level data to the computer in the car.
Most fluids are available as organic, synthetic, or mixtures of organic and synthetic fluids. It is recommended to follow the manufacturer's directions as to what type of gear oil to use, just don't follow the manufacturers "hint" that the gear oil has no expiration date.
In addition, seals can be squeezed out from this. Well, if you find flaws in time. Then you need to completely drain the resulting unpresentable composition and. And then fill in regular oil, the one recommended by the car manufacturer (as a rule, this information is in the service book or on the official website of the company). So, no initiative.
Facts and myths about transmission fluid
From left to right, the state of use transmission fluid: new, good, normal, limited, burnt, burned with pieces of metal. Many people do not neglect what can cost them thousands of dollars. There's so much misinformation out there with broadcasts that it's hard to know what to do. There are many myths about the broadcast service. This could cost you dearly. Here are some facts to clear up these myths and help you not to lose.
Myth: If I don't have my 000 km transmission, it may be too late or may cause it to fail. Proper transmission maintenance will never damage your transmission and can prolong its life, especially when you perform predictive and preventative maintenance. That is, a service that predicts fluid problems through appropriate equipment and predicts future problems.




