How to determine the direction of the tire. What is an asymmetric tire? From A to Z"
The tread pattern is one of the most important tire characteristics. The grip of the coated wheels, the removal of water from the so-called contact patch, that is, the place where the wheel touches the road, and the braking speed depend on it.
Naturally, the ideal pattern does not exist, otherwise there would not be so many types of them. There are different cars and their owners, as well as roads and weather conditions. Manufacturers are trying to take all this into account, and the current drawings can be divided into two types: non-directional and directional. And they, in turn, are symmetrical and asymmetrical.
It is also called classic, as it is more common.
Visual characteristics: the pattern is uniform over the entire surface.
Features and Benefits:
- tires have average performance in everything, that is, they behave best at medium speed and on dry or moderately wet surfaces. They have average cross-country ability on the primer, average stability during maneuvers. Do not produce loud noise and are easy to operate;
- tread properties do not change, no matter which way the wheel rotates. Therefore, they are allowed to be installed as you like;
- democratic price. They are most often equipped with most cars at the factory.
Flaws:
- behave poorly on wet roads, in rain and snow;
- unstable at high speed.

Visual characteristics: The right side of the picture is different from the left. In addition, there are special markings on the sidewalls.
Features and Benefits:
- the tread has two parts, and each is responsible for certain qualities: one ensures the stability of the car even at high speed, and the other is designed to push water out of the contact patch;
- the noise level is low, but this is a property of all non-directional protectors;
- the concept of the outer and inner sides appears, which are indicated on the sidewall by the inscriptions OUTER and INNER, respectively. Tires will have to be installed taking into account the marking: the left wheel cannot be put on the right side (and vice versa). In critical cases, you can resort to overboarding, but this is not always convenient. It is impossible to guess what kind of spare tire to carry with you. Experts advise taking the right wheel, since breakdowns most often occur from the side of the roadside.
Flaws:
- an installation error entails accelerated tire wear, and also adversely affects the controllability of the machine;
- high price.

Visual characteristics: deep drainage grooves are visible, the location of which resembles the letter V, as well as additional markings on the sidewalls.
Features and Benefits:
- are considered the most modern and technologically advanced. Manufacturers have decided that cars drive mainly on asphalt, so it is important to take care of wet stability. In such conditions, the safety of movement and maneuvering depends on the tread, so classic tires are gradually giving way to directional ones;
- when driving on hard surfaces, directional tires provide excellent directional stability;
- tires have a direction of movement, and this must be taken into account when installing. Typically, the manufacturer supplies their product with an arrow-shaped marking with the signature ROTATION indicating the direction, so it's hard to make a mistake.
Flaws:
- the noise level is higher than that of non-directional;
- at high speed maneuvering is difficult. Due to the outlets of the drainage grooves, the rigidity of the edges of the tires is reduced, the car can drive to the sides;
- due to soft edges not suitable for primer;
- an installation error will lead to rapid wear and deterioration of wet grip: the drainage grooves will not push out, but will rake in water.

This is the rarest type of tire.
Visual characteristics: in the figure, drainage grooves in the form of a half of the letter V are visible. The second half of the pattern also has them, but elements that reinforce the outer edge are also visible.
Features and Benefits:
- tires have a direction of rotation, which is indicated by an arrow on the sidewall. In addition, there is an inside and an outside. It is indicated by the markings INNER and OUTER;
- the inner side is designed for better grip on wet roads, while the outer side, with a stiffer edge, provides stability at high speeds.
Flaws:
- it is important to follow the markings when installing such rubber, because mistakes lead to increased wear and poor handling;
- tires have an inside and an outside, so the wheels can be either left or right. This creates difficulties when choosing a spare wheel: it is impossible to predict which wheel will be pierced;
- directional asymmetric tires are quite expensive.
Obviously, you need to choose a tire pattern, focusing on your driving style and the conditions in which it occurs. The price factor is also important: you should not overpay for unnecessary functions, but if life depends on it, it is better not to be greedy.
For example, asymmetric tires are more versatile, but more expensive than classic tires and make it difficult to choose a spare tire. Therefore, the driver who most often has to drive around the city, where there is not much acceleration, has every reason to prefer a non-directional symmetrical pattern.
On the other hand, a person who often has to drive on the track needs tires that are stable at high speeds even on wet surfaces. In this case, it is really worth forking out for asymmetric ones.
That is, best drawing tread is a matter of choice for every driver, and the perfect tire is still in development.
Fate brought me to Michelin Pilot Primacy tires, these tires are asymmetric, i.e. What matters is the inside and the outside. But if you look closely at the figure, you can see that on the same axis, the direction of the pattern (drainage grooves) has a different direction. This is what stumped me.
Michelin Pilot Primacy
When I started to "smoke" the problem on the Internet, I realized that this problem I'm not the only one concerned.
And the main reason for the "misunderstanding" is precisely that everyone is confused by the multidirectional tire pattern.
Found information that clears things up.
The representative office of Nokian Tires in Russia knows about the difficulties of some car owners with the installation of asymmetric tires and specifically provided information on installing "right and left" tires.
Officially from Nokian Tires: Asymmetrical non-directional tires are mounted on the principle of inside and outside. The corresponding marking can be found on the tire itself. OUTSIDE is the outer side of the tire, INSIDE is the inner side of the tire. According to this designation, the inside of the tire must be installed towards the car itself, and the outside - away from the car.
Since the tires are non-directional, there are no "right" and "left" tires for a car*. They are all the same and there is no difference in their direction of rotation.

As an addition.
Due to the large number of questions and concerns about "right and left" tires, especially about the Nokian Hakka i3 model, the answer is: right and left tires - no. The tire has an outer and inner side. Which are designated as Outside (external) and Inside (internal). Look for these designations on your tire.

GENERAL INFORMATION
The most important property of any tire is to ensure reliable grip on the road surface. This task is performed by the tread rubber, “fitting” due to its elasticity the microroughness of the road in the contact patch. In wet weather, even at low speeds, a water film forms between the tread and the road, preventing their contact with each other. To avoid loss of control under such conditions, it is necessary to drain water from the contact patch, therefore, both longitudinal and transverse grooves are made on the tread various shapes. In order to better remove dirt, which is more viscous than water, from the contact patch, the grooves must be wider.
However, with an increase in the number of grooves or their width, the load on the tread lugs increases and dry grip deteriorates, due to a decrease in the area of \u200b\u200bcontact of the rubber with the road. In addition, a large load on the tread lugs contributes to accelerated tire wear.
The characteristics of each particular tire are achieved through a complex combination of design features, tread pattern and the quality of the used rubber compounds. The noise level during rolling, wear resistance, and road grip depend on the tire tread and its pattern. Often, designers improve one or two parameters to the detriment of others, for example: they reduce noise and increase ride smoothness due to some decrease in stability and controllability.
It is impossible to achieve high scores for all indicators simultaneously with one type of tire. Therefore, the number and variety of produced tires and tread patterns cannot even be described, since more and more new original samples appear every year.
Learn more about tire markings:
DESIGNATION AND CLASSIFICATION OF TIRES
About driving with punctured tires:
DRIVING WITH A PURCHATED TIRE
About inflating tires with nitrogen or other gas:
INFLATION OF TIRES WITH GAS
TIRE TYPES
During operation passenger car in summer the most common road, all-weather and universal tire types. road tires(commonly called summer), are designed for use at positive temperatures on highways. Tires of this type provide the best grip on dry and wet hard surfaces, fuel efficiency, maximum wear resistance and the best way adapted for high speed driving. For driving on dirt roads (especially wet) and in winter, they are of little use. The tread pattern is distinguished by clearly defined longitudinal grooves to drain water from the tread contact patch with the road, weakly expressed transverse grooves and the absence of a micro-pattern. In addition, they have a mandatory smooth (rounded) transition from the tread to the sidewalls.
All season tires are a compromise between summer and winter tires, and therefore inferior to them in terms of traction when used in the corresponding season. They are adapted to work on dry and wet pavement, to winter roads, provide a good level of comfort and satisfactory efficiency, but they are somewhat more worn than summer ones.
One set of these tires provides an acceptable realization of the characteristics of the car during year-round operation. Tread pattern all season tire more branched, and the elements of the pattern are grouped into a well-defined "path" and separated by grooves of different widths. On large elements of the pattern there are narrow slots (lamellas) that provide grip on an icy or snowy road.
As a rule, these tires are marked all season, tous terrain or conventional signs(snowflake or drop).
Universal tires(according to domestic terminology) are designed to work on roads of any quality. Moreover, it can be quite difficult to draw a clear line between them and all-weather ones. They differ primarily in a deeper and more branched tread pattern.
The fact is that under the roads of "any quality" in the CIS, one can understand 60-80% of all roads, including off-road, so this type of tire is largely a domestic invention. By Western standards, tires of the M + S type (Mud and Snow - mud and snow) can be attributed to universal tires in a variant with a tread pattern less dissected by grooves, with a weakly expressed micropattern or without it.
Tread pattern
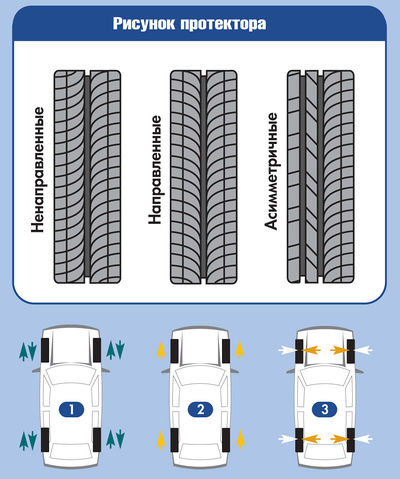
The tread pattern is formed by a certain arrangement of its elements relative to each other and the direction of tire rotation. Can be used on any type of tire non-directional, directional or asymmetric tread pattern, which has a significant impact on its performance.
1 - non-directional tire is installed on the car arbitrarily;
2 - the directional tire is installed on the car in the direction of the arrow on its sidewall;
3 - asymmetric tire installed on the car in accordance with the inscription on its sidewall:
"Outside"- outer side;
"Inside"- inner side
Omnidirectional the most versatile pattern, so some tires are produced with it. It allows arbitrary installation of the wheel and any direction of rotation of the tire, but is inferior to other patterns in its ability to intensively remove water from the contact patch with the road.
Directed the pattern is different in that its elements (simplified) diverge in a herringbone pattern, and this requires a certain direction of rotation of the wheel. This construction of the elements makes it possible to more effectively remove water and liquid dirt from the contact patch than with a non-directional pattern and reduce the level of noise generated by the tire when driving. On the sidewalls of tires with these patterns, the direction of rotation is necessarily indicated. A certain inconvenience is due to the fact that the "spare wheel" coincides in the direction of rotation only with the wheels of one side of the car, and on the other side it can only be used for a trip at low speed to the nearest tire service.
Asymmetric pattern is one way to implement different properties in one tire, for example, the outer side of the tread is made with a pattern that provides the best grip on a dry road, and the inner side with a wet one. It is characterized by a different arrangement of grooves and checkers on one side and the other from the middle of the tread. Tires with an asymmetric pattern are most often non-directional, and occasionally directional; in this case, different tires are required for the left and right wheels of the vehicle. On the sidewalls of tires with an asymmetric pattern, it is mandatory to indicate which side should be directed inward and which should be directed outward. If the set of tires has an asymmetric non-directional pattern, then the spare wheel fits on either side of the vehicle.
When choosing and operating tires, some general rules can be helpful.
Use the tire sizes recommended by the vehicle owner's manual.
Since there are no ideal tires, when choosing them, it is advisable for yourself to determine which properties, in addition to reliable grip, are most important - “sportiness”, comfort, economy, etc.
A road comfort tire with low noise and good ride quality may not provide good stability and handling on the road. high speeds.
The tire has an extended life and provides a reduction in fuel consumption (compared to other models) due to low rolling resistance, but may not provide good comfort.
As a rule, manufacturers indicate in their advertising brochures which the best properties has this model tires, but at the same time they are silent about what properties they “sacrificed” for this.
Choosing the parameters of tires when replacing them, you can improve some car performance, but certainly at the expense of reducing others.
Low profile tires will improve the car's handling, especially at high speeds, but they are more susceptible to damage on uneven roads.
Only external similarity or, conversely, differences between tires from different manufacturers do not allow us to draw an unambiguous conclusion about the similarity or difference in their performance properties.
All tires, even within the same type, differ in rubber chemistry, internal construction, and tread pattern.
Exploitation winter tires in the summer, in addition to their accelerated wear, it worsens directional stability, handling ("cotton steering wheel") and braking properties of the car.
SOME SYMBOLS ON TIRES
All season (Tous terrain)- All-season tyre.
M+S(mud and snow) - designation on tires for all-weather and winter operation.
rotation– direction of rotation (for tires with a directional pattern).
Side facing forwards or Inside– side facing inward*.
side facing or outside– side facing out*.
P (Passenger)- car tire (American).
Second, second(or DA) - the designation indicates the presence of secondary defects that do not affect the high-speed strength.
maximum pressure- maximum pressure. Load is in pounds (LBS) and pressure is in pounds per square inch (PSI) for the tire when cold (1LBS=0.4536kg; 1PSI=0.0069MPa)
TWI(Tread Wear Indication - wear indicator track) - a sign on the sidewall of the tire. Shows the location of the remaining tread height marks in the main grooves. This sign is applied near the tread evenly in six places around the circumference.
*Inscriptions that can be applied to the side of asymmetric tires. They indicate the orientation of the tire relative to the longitudinal axis of the machine when it is mounted on the wheel.
An asymmetric tread pattern is one of the most effective in all respects, but when buying it, you should take into account certain features and know how to install tires with an asymmetric tread pattern.
What is an asymmetric tread pattern
Tires belonging to this type, in Lately are increasingly used by automakers for installation on vehicles of a more expensive class. This is due to the fact that a car that has tires with such a pattern, at least, will not lose the high performance characteristics laid down by the manufacturer, and, as a maximum, will increase them.
When answering the question of what an asymmetric tread pattern means, this type should be distinguished from symmetrical tires. If you look at the rubber in relation to the center line drawn along the middle of the wheel around the circumference, you will find that each half has a pattern that is different from the opposite.
Tire manufacturers offer both winter and summer tires. Each type uses its own composition of the compound and pattern. They also differ in tread height (for summer it is less), the ability to install spikes (for winter tires).
Asymmetric pattern - advantages and disadvantages
The pros and cons of an asymmetric tread pattern are relative categories, but they, like all types of tires, take place. When choosing one or another protector option, it is necessary to take into account the following factors:
- car type;
- vehicle management style (calm, aggressive);
- features of operation (in the city, outside the city);
- regularity of use (year-round, seasonal).
The undoubted positive aspects include the high controllability of the car in rainy and snowy weather. That is why most motorists are installing with the onset of autumn. They are quiet and economical. The resource, like all other types of tires, depends on the driving style. But it should be noted that on the outside, a harder rubber is used, which allows you to confidently pass difficult fates at high speed.
If a choice is to be made and a symmetrical or asymmetric tread pattern is being considered, then it should be noted that the wheels with the latter can only be interchanged by installing them from front to back and vice versa. The diagonal option is possible only in extreme cases.
What is the difference between drawings

The asymmetric directional tread pattern is visually different from the symmetrical one. But the most significant difference is that tires with a symmetrical pattern have the same compound throughout. Asymmetrical tires on the outside use a denser layer of rubber, so the car is able to overcome corners at high speeds.
The asymmetric non-directional tread pattern is a universal solution to improve dry performance (outer part of the tire works). And to improve grip on wet surfaces and quickly drain liquid, the inside of the tire is designed.
The cost of rubber is one of the main factors that is decisive for many. Tires with a symmetrical pattern are often installed on budget cars even at manufacturers. However, high performance should not be required from them. But in terms of price-quality ratio, they are the most acceptable.
Installing asymmetrical tires
Tires with an asymmetric pattern according to international standards are marked accordingly. On one side of the tire, you can see the inscription “Outside”. This means that the assembled wheel is mounted in such a way that after installation on the car, the inscription is readable from the outside. Accordingly, the designation “Inside” should be located from the inside. For those who are guided by these designations, the question of how to set an asymmetric tread pattern very rarely arises.
A special orientation does not mean that tires with an asymmetric tread pattern cannot be installed in any other way. But with incorrectly oriented wheels, the manufacturer does not recommend moving at a speed of more than 80 km / h. Also in this case, the declared technical properties of rubber will not be used in full.
Installing a tire with an asymmetric tread pattern necessarily requires balancing work with the wheel removed, and, if possible, also on the car. If the adjustment is carried out on a modern laser machine, the last procedure can be omitted.
Symmetric and asymmetric tires differ in tread pattern. Also, asymmetric tires can have different rigidity of the inner and outer sidewalls. The main advantage of asymmetric tires is greater cornering stability. This is achieved due to the fact that their outer sidewall and tread blocks on the outside are more rigid than on the inside. As a result, the loads in the contact patch of the tire with the road are more on the outside. This kind of expands the track and makes the car more stable. This is especially noticeable during high-speed maneuvering.
The tire tread has two types of grooves: longitudinal and transverse. The longitudinal grooves are designed to resist lateral forces (They hold the vehicle's course). The transverse ones counteract the longitudinal forces (they do not allow the wheels to slip). A typical variant is four or five wide longitudinal grooves and the same number of narrower transverse ones. In total, there are several dozen transverse grooves on the tire, but only five to eight are located on the contact patch at the same time. Why are asymmetric tires better than symmetrical ones?
The same number of grooves can work with different efficiency. It depends on their transverse profile and configuration. The best summer tires has transverse grooves of a curvilinear profile: "herringbone" or wavy. With this configuration, they are longer and the adhesion area, respectively, is also larger. Summer tires do not always work in dry conditions. On wet roads, special drainage grooves are important. On summer tires they are almost always present. In the winter they are made even more.
The number of grooves can be increased by widening the contact patch by using a wider tire. Usually the design of the hubs and brake mechanisms allows you to install discs with a positive reach. Tires on such disks are the widest. The disadvantage of this solution is that it greatly increases the wear of the hub bearings. Therefore, it is recommended to use it only in extreme cases, when all other methods of increasing stability have already been applied. Wide tires are almost always low profile. They further increase stability by reducing ground clearance.
Asymmetric tires are not much more expensive than symmetrical ones, and they are more suitable for high-speed maneuvering. Its only drawback is the difficulty of using a spare tire, since it is not clear on which side it is better to take a spare tire on a wheel. As a positive point in favor of asymmetric rubber, it can be noted that it lasts longer than usual on the front axle. Wheel alignment causes increased tread wear on the outside, and on asymmetric tires it is more rigid.




