What is a gur in a car. Hydraulic power steering (GUR) in a car
Today I will talk about power steering(GUR). From this article you will learn what power steering is, what you need to watch out for when operating a car with power steering? And what should you pay attention to when buying a car if it has a power steering?
Hello, dear readers blog.
hydraulic booster steering (GUR) - this is the hydraulic part of the steering mechanism, which serves to facilitate driving. As you understand, the name is directly related to the principle of action. The use of power steering on cars began with trucks. And this is understandable. Imagine how much effort it takes on the steering wheel to turn such huge wheels on a heavy car. And the power steering allows you to turn the steering wheel with one finger.
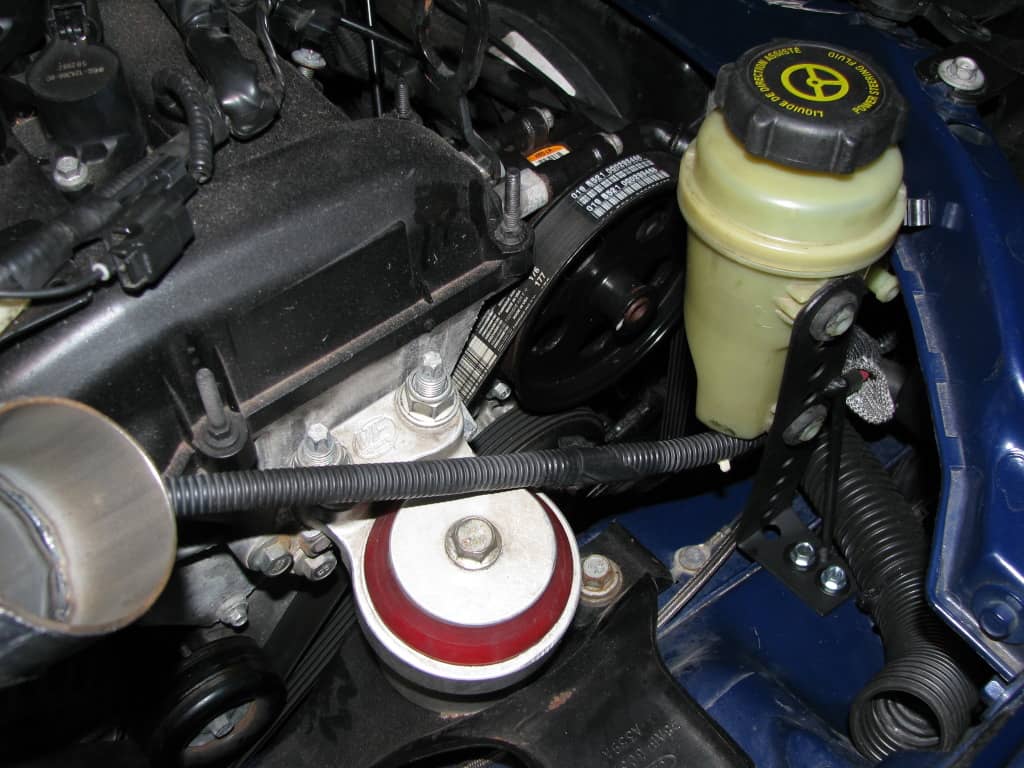

The power steering is a system consisting of
1) a pump that creates pressure and circulation of oil in the system;
2) a distributor that distributes the oil;
3) a hydraulic cylinder that converts oil pressure into the movement of a piston and rod, which in turn turns the wheels through a system of levers;
4) special oil, which transmits force from the pump to the hydraulic cylinder and lubricates all friction pairs.

The tank serves as a reservoir for oil. There is a filter in the tank, and a dipstick in the plug for determining the oil level (not for all machines). When you start the car engine, the belt starts to rotate the power steering pump, and the steering wheel becomes easy to turn.
You can check how hard it is to turn the steering wheel without power steering
To do this, do not start the engine and try turning the steering wheel. The hydraulic power steering not only provides comfortable and easy steering, but also increases driving safety. During the operation of the power steering, the shocks transmitted to the steering wheel from road irregularities are softened. It helps to hold the steering wheel if the front wheel is punctured at speed.

If you have a power steering on your car, then you can always keep the car on the trajectory you need (the steering wheel will not break out of your hands). Important indicator good hydraulic booster steering wheel is the presence feedback, the so-called sense of the road. In practice, than more expensive car, the better the feedback due to the power steering design, and vice versa.
When you turn the steering wheel, there is feedback from the steered wheels through the hydraulic booster to the steering wheel. You feel that, for example, on a slippery road, the steering wheel turns easier than on a dry one. And this feeling allows the driver, through the feeling of the road surface, to correctly rotate the steering wheel in any conditions. Without this feedback (if the steering wheel always rotated with the same effort), it would be difficult for the driver to determine the direction of the steered wheels.
Cons of power steering
But despite the large number of advantages and low cost in production, the power steering has many disadvantages. The power steering works directly from the engine. Thus, it takes some of the power from the engine, even when the car is driving straight or standing still, and the driver is not turning the steering wheel. If your car is equipped with power steering, then you should know that you cannot hold the steering wheel in extreme positions for more than 5 seconds. Because in extreme positions, the oil overheats, and the power steering may fail.

It is also undesirable to gas with the wheels turned out. It is necessary to monitor the oil level in the tank, change the oil in time, check the condition of the belt that drives the power steering pump, monitor oil leaks. And a car with power steering has poor feedback from the road at high speeds (the steering wheel is light).
All these shortcomings are devoid of electric power steering (EUR). But in any case, driving a car with power steering is much more comfortable than without it. If the power steering belt breaks, you will still be able to control the car, only the steering effort will be heavier, but you will be able to continue driving and get where you need to go, but without comfort. After this, do not over tighten with the replacement of the belt, because the power steering gear is designed to operate under oil pressure. And if the pressure drops (belt break), then an increased load will act on the parts of the steering mechanism, and the steering will quickly fail.
What should be monitored in the daily operation of the car?
Periodically (you can combine checking the power steering system with checking the engine oil), you need to check:
1) oil level in the hydraulic booster reservoir (by marks between min-max or by dipstick level).

To do this, you unscrew the reservoir cap (the engine is off) and look at the oil level on the dipstick built into the reservoir cap;
2) inspect the belt that sets the power steering in motion for cracks, delaminations, slips;
3) monitor the tightness of the system. Inspect the entire system for leaks, if there are oil leaks, then they must be eliminated, since without oil the steering mechanism quickly fails and its repair will be expensive. Easier to monitor and fix in time;
4) Replace the filter element and fluid once every 2-3 years. Change the oil if its color has changed or it has become cloudy;
5) special attention should be paid to the power steering if vibration is felt on the steering wheel, the car does not obey the steering wheel when cornering, or the steering wheel does not work correctly when the air conditioner (climate control) is turned on, or the steering wheel is hard to turn;
6) in winter very coldy when the oil is thick, do not hold the steering wheel in extreme positions and avoid hard taxiing when the car is not warmed up.
Please watch the power steering!
It's easy - open the hood and look at the power steering system and it will take no more than 3 minutes.

It does not require special knowledge to see leaks or look at the dipstick. The power steering is a fairly reliable mechanism and, most often, the reasons for its failure are improper operation (the steering wheel is held for more than 10 seconds in extreme positions) and insufficient control (the driver rarely opens the hood and does not monitor the oil level in the power steering reservoir and does not change it on time oil, filter and belt).
What to look for when buying a car equipped with power steering?
The main malfunctions of the power steering can be determined on the spot, without leaving the inspected car on the road. When buying, open the hood of the car and carefully look into the engine compartment. Watch out for oil leaks around the steering gear. Unscrew the power steering reservoir cap and look at the dipstick (if any).
There are marks on the dipstick or on the tank itself and the oil level must not be lower than these marks. Drop a drop of oil from the dipstick onto some surface (you can use your finger) and look at this drop. The oil must be clear (no cloudiness) and free from impurities, the color must be determined. Screw back the power steering reservoir cap. Inspect the belt that drives the power steering. There should be no cracks, delaminations on the belt, protruding threads of the belt cord are not allowed.

A car without steering is quite difficult to imagine. But at the dawn of the automotive industry, there was such a thing. When heavy vehicles began to appear, one problem arose: in order to unscrew at low speeds, one had to make simply titanic efforts. Therefore, design engineers were puzzled by the issue of facilitating this process.
The brainchild of their brilliant thought was the power steering. At first it was vacuum and did its job rather poorly, then it appeared, and the electronic amplifier was the pinnacle of technological progress. If in the second one oil is used as a working fluid, then in the third one the microcomputer analyzes the steering angle, after which it rotates the wheels with the help of an electric motor. Today we will talk about power steering, its features, principle of operation and some points that will significantly increase its service life.
General position
The device and principle of operation of the power steering consists of the following elements:
- pump;
- distributor;
- , which transmits force to the wheels;
- filling tank.
And now let's look at the points, how the power steering works:
- When turning, the valve installed in the distributor opens or closes. Allowing the oil to flow one way or the other.
- The power steering pump is driven by the car's engine through a belt.
- Depending on which way the steering wheel is turned, the oil supply valve opens or closes, freeing or filling a special reservoir.
- Depending on the degree of filling of the tank, the wheels turn in one direction or the other.
As you can see, everything is very simple.
But, in fact, the hydraulic booster is a rather complicated device. Therefore, it requires regular maintenance.
If you do everything right and constantly change the oil in the system, then the power steering will last long years. But, if done incorrectly, this device can be ruined in 5 seconds!
pump belt
The most complex device in the entire power steering system is the power steering pump and its belt. It consists of many small parts, which in theory should serve happily ever after, but some owners can break down very quickly.
The impeller, which contains the power steering pump, rotates constantly, which creates a continuous flow of oil. It is driven by a belt thrown over the shafts of the engine and the power steering itself. They spin at the same speed no matter how fast the car is going.
And here lies another interesting point: during idle time, that is, when the engine is turned off, the hydraulic booster will not work!
It often happens that the belt wears out over time. And then the worst thing happens - the control suddenly becomes very tight, because the driver has to turn the wheels on his own. It is possible to cope with this situation, but at first it seems as if the steering wheel is jammed. Often, this second is decisive! And some drivers start to panic and even after some time they do not understand that it is still possible to turn the wheels. As a rule, this leads to an accident.
Turning wheels and deadly 5 seconds
As a general rule, modern power steering can fail if you keep the steering wheel turned for 5 seconds. During this time, such pressure is created in the tank that they break. So watch this moment.
Characteristics of hydraulic boosters
The most main characteristic- this is the speed of the response of the hydraulic booster to the steering wheel. In good systems, it is 0.1 - 0.2 seconds, that is, it reacts almost instantly. If you ordered a Chinese system, then save yourself from possible accidents - do not install it! There were cases when the response time of the device reached 1-2 seconds! As you can see, this is a lot.
The next is smoothness. This is also a very important characteristic of the hydraulic booster, because when the car turns jerky, the consequences will not only be unpleasant sensations for passengers. Other precise mechanisms installed in the vehicle may be affected.

Working move. If it is insufficient, then the car simply will not be able to turn around as sharply as it was intended by the designers.
How to change the oil in the power steering
There is nothing complicated in this:
- Through the filler neck of the barrel, select the used oil with a syringe (change it every year or two).
- Now remove the return tube from the barrel and place a container under it.
- Turn the steering wheel in different directions. The power steering pump must not be driven by the motor. Better car completely muffle or remove the belt from the power steering shaft.
- After the return hose stops spraying oil when turning the steering wheel, put it back on. Also wear a belt.
- Now fill the system with oil. Pour until it stops leaving the keg.
- Turn the steering wheel and check the keg. If oil is still leaking, add it.
- Start the engine and turn the steering wheel again. It should spin easily.
- Shut off the engine and look into the barrel again. Top up if required.
Do-it-yourself power steering repair
Remember, the hydraulic booster is a very precise mechanism, most of the breakdowns of which can only be done in specialized auto repair shops. But, some breakdowns can be “cured” on their own:
- Overheat. Most likely there is not enough oil in the system.
- The appearance of dust and dirt. Remove the tubes and flush them.
- Liquid leakage. The pressure is too strong and the clamps that secure the pipes cannot provide a reliable connection.
- The wheel began to spin with difficulty. Change the fluid in the system in time.
- Bending or fracture of the tubes. For the lines of the power steering system, special hoses must be selected, since the pressure in them is very high.
- Pump
Every modern car has a power steering. The pressure of the working fluid for the operation of the power steering is created by a special pump - read the article about the purpose of the power steering pump, the types of pumps that exist today, their design and operation, as well as maintenance and repair.
General power steering device
In any modern car and wheeled tractor, there is always a system that greatly facilitates the work of the driver - power steering (GUR). Amplifier built directly into steering, allows the driver to spend less effort when turning the steering wheel, increases the controllability and safety of the vehicle in any conditions.
The power steering device depends on its type; at present, three main types of hydraulic boosters can be distinguished:
- Power steering with a separate steering mechanism and a power hydraulic element;
- Power steering with a combined steering mechanism and a power hydraulic element;
- Rack and pinion power steering, combined with steering gear rods.
The hydraulic booster with a separate steering mechanism and a power element includes a pump, a switchgear, a power hydraulic cylinder, a reservoir for working fluid, a piping system and some auxiliary elements. In this case, the power cylinder is connected to the steering gear or directly to the wheels, and minor changes are made to the regular steering.
The hydraulic booster with a combined steering gear and power element includes a steering gear with an integrated switchgear and a hydraulic cylinder, a pump, a reservoir, pipelines and additional elements. As in the first case, the steering force is transmitted to the steering gear with the help of additional traction.
Rack power steering is further development hydraulic boosters with a combined steering mechanism and a power element. The rack includes transverse steering rods, and a gear-rack pair is used as a gearbox (from where this mechanism got its name). Typically, racks are used on front-wheel drive cars, although in last years these mechanisms are increasingly being installed on commercial trucks and vans.
In all these types of power steering, fundamentally the same pumps are used, which need to be discussed in more detail.
Purpose and place of the pump in the power steering system
The hydraulic booster system uses oil as a working fluid, which is supplied to the actuator under pressure. just what is needed to create a working oil pressure in the system.
The power steering pump is installed on power unit vehicle, for which a special bracket or mating surface is provided. The pump is driven by the engine crankshaft, the drive can be one of two types:
- V-belt transmission;
- Gear transmission.
V-belt drive, in turn, is of three types:
- One V-belt;
- Dual V-belt;
- V-ribbed belt.
A drive with a single V-belt is rarely used today; it can be found on GAZelle, VAZ-2121, etc. cars. The double belt drive is more often used in domestic trucks. Poly V-belt is used on passenger cars, vans and commercial trucks.
The gear drive of the power steering pump is used on trucks. It is more complex, since the engine must initially be developed for a specific type of pump. The pump drive in this case is also carried out from the crankshaft, however, the torque is directly transmitted to the pump gear from one of the gears of the drive of the engine units.
Despite the variety of pumps, they all have a fundamentally the same device.
Types and design of pumps used in hydraulic boosters
At present, double-acting vane (vane or vane) pumps are most widely used (letters "L" or "Sh" are usually present in the marking of domestically produced pumps). Such pumps the best way work with a viscous incompressible fluid, have high performance and reliability, and at the same time have a fairly simple device.
The basis of the pump is made up of three components - a rotor with movable plates, a stator and a distribution disk. The rotor is inserted inside the oval hole of the stator, and the whole structure is mounted on a sealed housing or pump housing cover. On the opposite side, the rotor and stator are closed by a distribution plate with windows located in a special way. The rotor is mounted on a shaft, through bearings installed in the housing, outside the pump, the shaft ends with a pulley or gear. The package of the body, stator and cover is pulled together with four bolts.
The pump contains a number of additional components - several valves (bypass, safety or pressure), sensors, seals and o-rings, fittings, pipes, etc.
It should be noted that today there are two types of power steering pumps that differ in layout and placement of the oil tank:
- With a tank mounted on the pump;
- With a remote tank (placed in the engine compartment).
In trucks KAMAZ, GAZ, ZIL and others, power steering pumps integrated with a reservoir are widely used. But today, pumps with a remote tank are more common, due to the convenience of the layout of the units on the engine and in the engine compartment, as well as the convenience of servicing the hydraulic booster.
The principle of operation of the power steering pump
The vane pump works quite simply. The rotor, inserted into the stator with an oval hole, forms two closed crescent-shaped cavities, into which there are two windows - through one of them oil is supplied from the tank, and through the other it enters the system under pressure. The blades (gates) are installed in the rotor with a certain gap (without interference), so they can move freely along the grooves of the rotor up and down.
When the rotor rotates, the blades move out of their slots under the action of centrifugal force and abut against the stator, as a result of which a number of sealed cavities are formed between the blades. Since the stator has an oval shape, when the rotor rotates, the volume of the cavities is constantly changing - this is the basis for the principle of operation of the pump.

The oil supply window to the rotor is located in the area of the expansion of the stator cavity, here it is captured by the expanding cavity between two adjacent plates. The flow of oil into the cavity is ensured by their expansion - with an increase in volume, air rarefaction is formed, as a result of which the oil is sucked into the cavity, completely filling it. The same effect ensures the flow of new oil from the reservoir to the pump.
With further movement, the cavity with oil leaves the inlet window and becomes airtight. But soon a tapering section of the stator begins, on which the blades are pressed into the rotor and the volume of the cavity decreases. Since the cavity is sealed, the oil contracts and its pressure rises. At a certain point, the cavity approaches the outlet port, and pressurized oil escapes through it into the system. Some of the oil under pressure is fed into the grooves of the rotor blades, which ensures a more reliable pressing of the blades to the stator walls.
Since the hole in the stator has an oval shape, crescent-shaped cavities are formed on both sides of the rotor, and the processes described above occur in each of them. That is why pumps of this design are called double-acting pumps.
The release of oil from the pump is carried out through a calibrated hole, which has a limited throughput. With an increase in the crankshaft speed, the performance of the power steering pump increases, however, all the oil does not have time to exit through the calibrated hole, it flows through the channel to the bypass valve, when the critical pressure is reached, the valve opens and directs the oil either to the pump inlet or to the tank. This prevents an uncontrolled increase in pressure in the system by high revs motor.
However, the pressure can increase not only due to an increase in the frequency of the engine, but also for other reasons - due to various blockages or breakdowns. With an excessive increase in pressure in the pump, a safety valve opens, which also diverts the working fluid to the pump inlet or reservoir. Modern pumps often use sensors and electric actuators to control valves.
Issues of maintenance and repair of power steering pumps
Requires minimal maintenance - it is necessary to monitor the appearance of leaks, fastening the pump and tensioning its belt. Typically, the pump serves several hundred thousand kilometers and requires intervention only when malfunctions occur.
Most often, the following malfunctions occur in the pump: wear of bearings, rotor and blades, sticking or complete loss of valve performance, wear of seals. All this is manifested by a deterioration in the operation of the amplifier, and the wear of parts gives itself out as knocks and increased noise. It is also harmful for the pump to lower the oil level and air the system, this is also manifested by increased noise.
A faulty power steering pump, especially with worn parts, is easiest to replace as an assembly, and most modern pumps do not even provide for disassembly and repair. After replacing the pump, air must be removed from the system, and after a simple adjustment, the power steering starts to work normally.
The hydraulic power steering (GUR) not only provides comfort, but also increases traffic safety. It helps the driver to maintain control of the car even in the event of a blown front tire. The reliability of this expensive device depends on timely maintenance.
The need to reduce the effort applied by the driver to the steering wheel led to the appearance of amplifiers, which is especially important for trucks. Even with a complex device and, as a result, high cost, hydraulic boosters are widely used due to the fact that, in addition to the main function (gain), they:
- allow you to reduce the gear ratio of the steering mechanism. This reduces the number of turns of the steering wheel between its extreme positions and, accordingly, increases maneuverability;
- soften the shocks transmitted to the steering wheel from bumps in the road, reducing driver fatigue and helping to hold the steering wheel in the event of a front tire burst;
- retain the ability to drive a car when the amplifier fails;
- provide a "feel for the road" and kinematic follow-up action (see below).
Power steering device
The power steering (Fig. 1) is a hydraulic system consisting of the following elements.
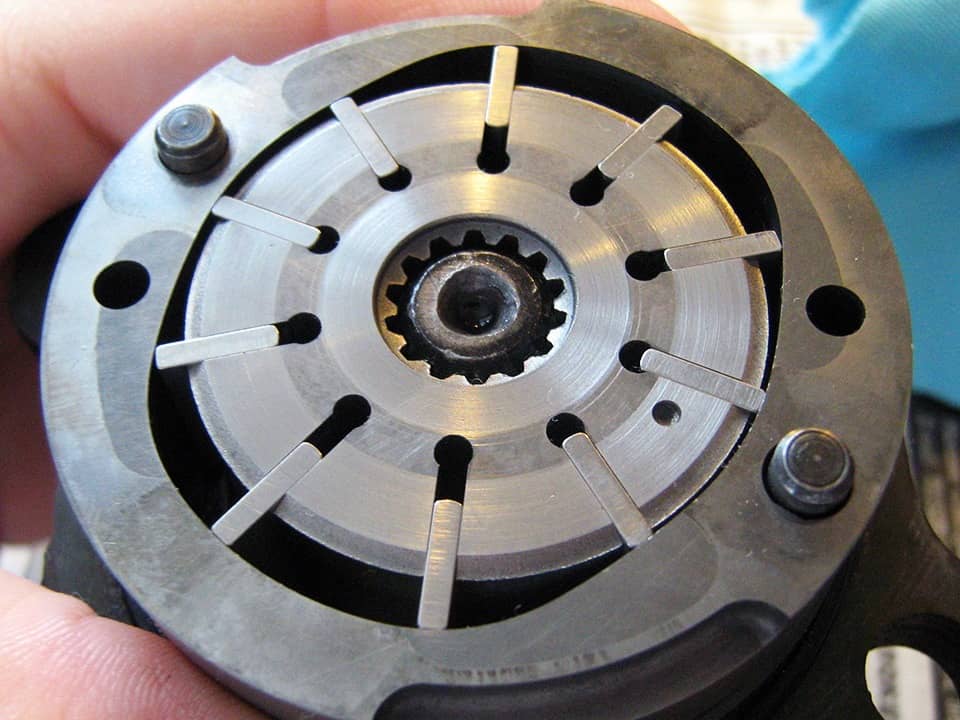
Pump provides pressure and circulation of the working fluid in the system. The most widespread are vane pumps (Fig. 2) due to their high efficiency and low sensitivity to wear of working surfaces. The pump is mounted on the engine, and its drive is carried out by a belt drive from the crankshaft.
Distributor directs (distributes) the flow of fluid into the required cavity of the hydraulic cylinder or back into the tank. If its spool (movable element) moves forward at the same time, the distributor is called axial, if it rotates, it is called rotary. It can be located on the elements of the steering drive or on the same shaft with the steering gear. The distributor is a precision (high-precision) assembly that is very sensitive to oil contamination.
hydraulic cylinder converts fluid pressure into movement of a piston and rod, which turns the wheels through a system of levers. It can be built into the steering gear or located between the body and steering gear elements.
Working fluid(special oil) transmits force from the pump to the hydraulic cylinder and lubricates all friction pairs. The tank serves as a reservoir for liquid. It contains a filter element, and in the plug there is a dipstick for determining the level.
Connecting hoses provide fluid circulation through the amplifier system. High pressure hoses connect the pump, distributor and hydraulic cylinder, and through low pressure hoses, liquid enters the pump from the tank and returns to it from the distributor.
IN modern cars an electronic unit (not shown in the figure) adjusts the operation of the hydraulic booster depending on the speed. This further increases safety at high speed, as it is more difficult for the driver to turn the steering wheel sharply (involuntarily) and, accordingly, deviate the car from the trajectory.
Scheme of work of power steering
The operation of the hydraulic booster with an axial distributor (without an electronic unit) is schematically shown in fig. 2.
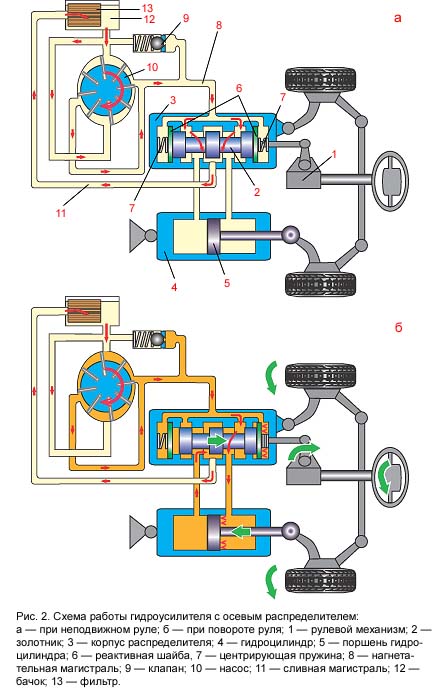
With the steering wheel stationary(Fig. 2, a) the spool is held in the middle (neutral) position by centering springs. The cavities of the distributor are interconnected so that the liquid flows freely from the discharge line to the drain line. The booster pump only works to pump fluid through the system, and not to turn the wheels.
When turning the steering wheel(Fig. 2, b) the spool moves and blocks the drain line. Oil under pressure enters one of the working cavities of the cylinder. Under the action of the fluid, the piston with the rod turns the wheels. They, in turn, move the distributor body in the direction of movement of the spool. As soon as the steering wheel stops turning, the spool stops and the body catches up with it. The neutral position of the distributor is restored, at which the drain line opens again and the rotation of the wheels stops. This is how the kinematic follow-up action of the amplifier is implemented - ensuring the rotation of the wheels at an angle set by the driver when the steering wheel is rotated.
"Road Feeling"- This is feedback from the steered wheels through the amplifier to the steering wheel. Provides information about the conditions under which the wheels turn. To do this, as in a car without an amplifier, on a slippery road the steering wheel should turn easier than on dry pavement. "Road Feeling" (power follow-up action) helps the driver to operate the steering wheel correctly in all conditions. For its implementation, plungers, chambers or reaction washers are provided in various designs of distributors (Fig. 2, b). The greater the resistance to turning the wheels, the higher the pressure in the cylinder and distributor. In this case, one of the reactive washers with great effort tends to return the spool back to the neutral position. As a result, the steering becomes "heavier".
When hitting an obstacle(for example, a stone) it affects the steered wheels, trying to turn them, which is especially dangerous on high speeds. The wheels, having started a forced turn, move the distributor body relative to the spool, blocking the drain line. Pressurized oil enters the cylinder cavity. The piston transmits force to the wheels in the opposite direction, preventing them from turning any further. Since the stroke of the spool is small (about 1 mm), the car will hardly change direction. The hydraulic booster not only makes it easier for the driver to turn the wheels, but also protects his fingers from being hit by the steering spokes when hitting obstacles. A slight push on the steering wheel will still be felt due to reaction washers, the pressure over which will increase.
If the pump stops working(for example, if the drive belt breaks), the ability to drive the car is retained. The force from the steering mechanism in this case will be transmitted by the spool itself to the distributor housing and further to the wheels. The liquid, flowing through the bypass valve (not shown in the diagram) from one cavity of the hydraulic cylinder to another, will practically not prevent the wheels from turning. But since the hydraulic booster does not work, the steering wheel becomes “heavier”.
The principle of operation of a hydraulic booster with a rotating (rotary) spool is similar to that described above.
In order for the hydraulic booster not to fail ahead of time, it is necessary to monitor its performance - if it is normal, the force on the steering wheel will be much less than when the engine is turned off, and also follow the requirements of the vehicle operating instructions and carry out the following operations:
- check the oil level in the tank;
- monitor the tightness of the system and eliminate various leaks as soon as possible;
- check and, if necessary, adjust the tension of the drive belt;
- change the filter element and oil once every 1-2 years. It is also necessary to replace them if the color of the oil has changed.
In order to avoid the failure of their failure of hydraulic booster parts unacceptable:
- hold the steering wheel in the extreme position for more than 5 seconds - this can cause the oil to overheat;
- long-term operation of the car with an idle pump - this leads to rapid wear of the parts of the steering mechanism and distributor, since they are not designed for this mode.
When the first signs of a malfunction appear, it is necessary to establish the cause and, if possible, eliminate it as soon as possible.
Power steering units require qualified personnel and high-precision equipment for repair, so it is possible only in specialized workshops. The feasibility of repairing or replacing a node is determined by its price. In most cases, it is more profitable for domestic cars to purchase a new unit, for foreign cars - repair
Some car owners are interested in the question: how does the power steering work. The principle of operation of the power steering is to facilitate driving. Its need has been brewing for many years. Previously, cars were light, and drivers did not need help in driving them, but with the advent of trucks, buses and other heavy equipment, power steering has become a necessity, because turning the wheels of a multi-ton car is not an easy task even for a strong man.
Later, passenger cars were also equipped with power steering, where the device took root perfectly. Now, instead of turning the steering wheel with two hands, we can do it with one finger. The comfort and safety of trips has become higher, because now you need to make less effort to maneuver in an emergency.
Power steering device
The power steering is a closed, interconnected hydraulic system of components, consisting of:
- pump.
- distribution device.
- Hydraulic cylinder.
- Back.
- High and low pressure hoses.
Pump
The main part of the power steering design is the pump. With its help, pressure is created in the power steering and oil circulates in the system. It is fixed near the engine, and is driven from the crankshaft, using a belt or gear transmission (drive). The most common type of pump is vane, usually vane, it provides high wear resistance and high efficiency. However, it has a weak link, namely the bearing, which is why it has to be repaired. The pressure in pumps of this type is about 150 bar, which is very high.
Distributor
 The distributor in the power steering is a kind of adjuster that directs oil from the reservoir to the hydraulic cylinder and vice versa. It can be installed both on the steering gear shaft and on some parts of the steering gear. There are two types of distributor:
The distributor in the power steering is a kind of adjuster that directs oil from the reservoir to the hydraulic cylinder and vice versa. It can be installed both on the steering gear shaft and on some parts of the steering gear. There are two types of distributor:
- axial - if the spool makes translational movements;
- rotary - if it makes rotational movements.
hydraulic cylinder
Or as the power cylinder is also called, it performs the function of turning the wheels. The fluid in the power steering presses on the piston under pressure and causes the rod to extend, which causes the wheels to turn. In order to push the stem back, fluid with reverse side presses on the piston and the wheels return to their original position. The hydraulic cylinder can be located both on the steering gear and between the steering gear and the car body.
Tank
 A reservoir for the working fluid, which ensures the operation and lubrication of all power steering binders. It contains a special filter to avoid dirt ingress, since the distributor is very sensitive to this. To check the oil level there is a special dipstick and marks on it. The tank is located under the hood, usually in a prominent place next to the antifreeze tank and has a cylindrical shape.
A reservoir for the working fluid, which ensures the operation and lubrication of all power steering binders. It contains a special filter to avoid dirt ingress, since the distributor is very sensitive to this. To check the oil level there is a special dipstick and marks on it. The tank is located under the hood, usually in a prominent place next to the antifreeze tank and has a cylindrical shape.
High and low pressure hoses
Of course, the entire circulation of fluid through the power steering system is provided by hoses, which are divided into:
- high pressure hose;
- low pressure hose.
The high pressure power steering hoses circulate oil between the pump, the rotary or axial distributor and the hydraulic cylinder. And low pressure returns this oil from the distributor to the tank, as well as from the tank to the pump. It is important to monitor the condition of the hoses to avoid fluid leaks and breakage of the entire mechanism.
The principle of operation of the electric power steering
The power steering pump is driven by the vehicle engine and creates hydraulic pressure. The pump rotor is driven and rotates at the speed of the motor. Due to centrifugal force, the plates located in the grooves of the rotor are extended and held on the inner surface of the pump. The gap between the plates and the inner surface of the pump varies depending on the speed of the motor. This changes the volume of liquid pumped by the pump.
Power steering is a complex system that constantly works when the engine is running. If the car does not turn, then the spool is in a quiet (neutral) position. And the liquid circulates freely in the system. When the steering wheel is turned in one direction or another, the spool moves in the same direction, as a result of which one of the highways is blocked.
Under the pressure of the fluid, the piston of the hydraulic cylinder squeezes out the rod, and the wheels turn. As soon as the steering wheel returns to its original position, the spool takes up a neutral position. Through the second drain line that opens, the oil equalizes the pressure in the piston and returns the drain back.
Electric power steering
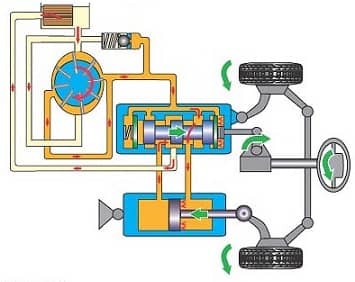 The main difference between the electric power steering is that the operation of the hydraulics is not connected with the crankshaft of the engine, but with an electric motor, which is powered by the car's battery.
The main difference between the electric power steering is that the operation of the hydraulics is not connected with the crankshaft of the engine, but with an electric motor, which is powered by the car's battery.
The so-called hybrid has become a logical continuation of the power steering. It is more economical and reliable. After all, the energy for the hydraulic pump does not come from the engine, but from the electric motor. The purpose of the electronic unit is to independently adjust the rotation of the hydraulic pump, depending on the readings of the speed sensor and the steering wheel sensor.
Reliability is ensured by a protection device in the electronic unit. It prevents the power steering from being reactivated in the event of a malfunction. Thus, protecting against serious damage. To unlock, you need to turn off the ignition and turn it on again after fifteen minutes.
The power steering with an electric motor is based on three modes:
- comfort;
- ordinary;
- sports.
With this approach, the feeling of the road (feedback) is greatly increased. This has a positive effect on the safety of driving at high speeds. It is worth noting that even if the engine breaks down, the EGUR will work, which will make it easier for you to transport it.
Outcome
The power steering device is complex and unreliable due to the high pressure in the system. However, on this moment only it makes it easier to drive heavy vehicles. Which makes it indispensable in some cases. The undeniable pluses include this transmission of high effort when turning the steering wheel.




